Deep Dive Android
Slide 1

Slide 2
Agenda ● Introduction to Android ● Android Tamer ● Application Architecture ● Pentesting ● Pentesting with Android
Slide 3

Trainer Profile Anant Shrivastava working at 7Safe as a Information Security Consultant. Primary focus area’s include Web and mobile. Certifications : RHCE, CEH, SANS-GWAPT Speaker / Trainer : Nullcon, ClubHack, c0c0n Active member of Null and Garage4Hackers http://anantshri.info anant@anantshri.info
Slide 4

Introduction
Slide 5
Agenda What is Android? The system architecture The application model The security model Custom ROM’s ADB Getting the Android source Setting up the environment
Slide 6
Android • Android Inc. founded in 2003 in Palo Alto, California by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears and Chris White. • Acquired in August 2005 by Google Inc. Key employees retained. • Design continued on a Linux powered mobile device. Marketed by Google to carriers as a flexible and easily upgradable OS. • On November 5, 2007, a consortium of mobile operators, software companies commercialization companies, semiconductor companies and handset manufacturers formed the Open Handset Consortium, with the stated aim of developing open standards for mobile devices. • On the same day, they released their first product …….…. Android.
Slide 7
Why Android 56% Smartphone market share – Gartner May12 Sources Available free of cost Minimal license cost for developers. Easy to setup development environment. Based on Linux App-stores filled with large number of apps. By 2014, mobile internet to take over desktop internet usage (Source: Microsoft Tag, 2012)
Slide 8
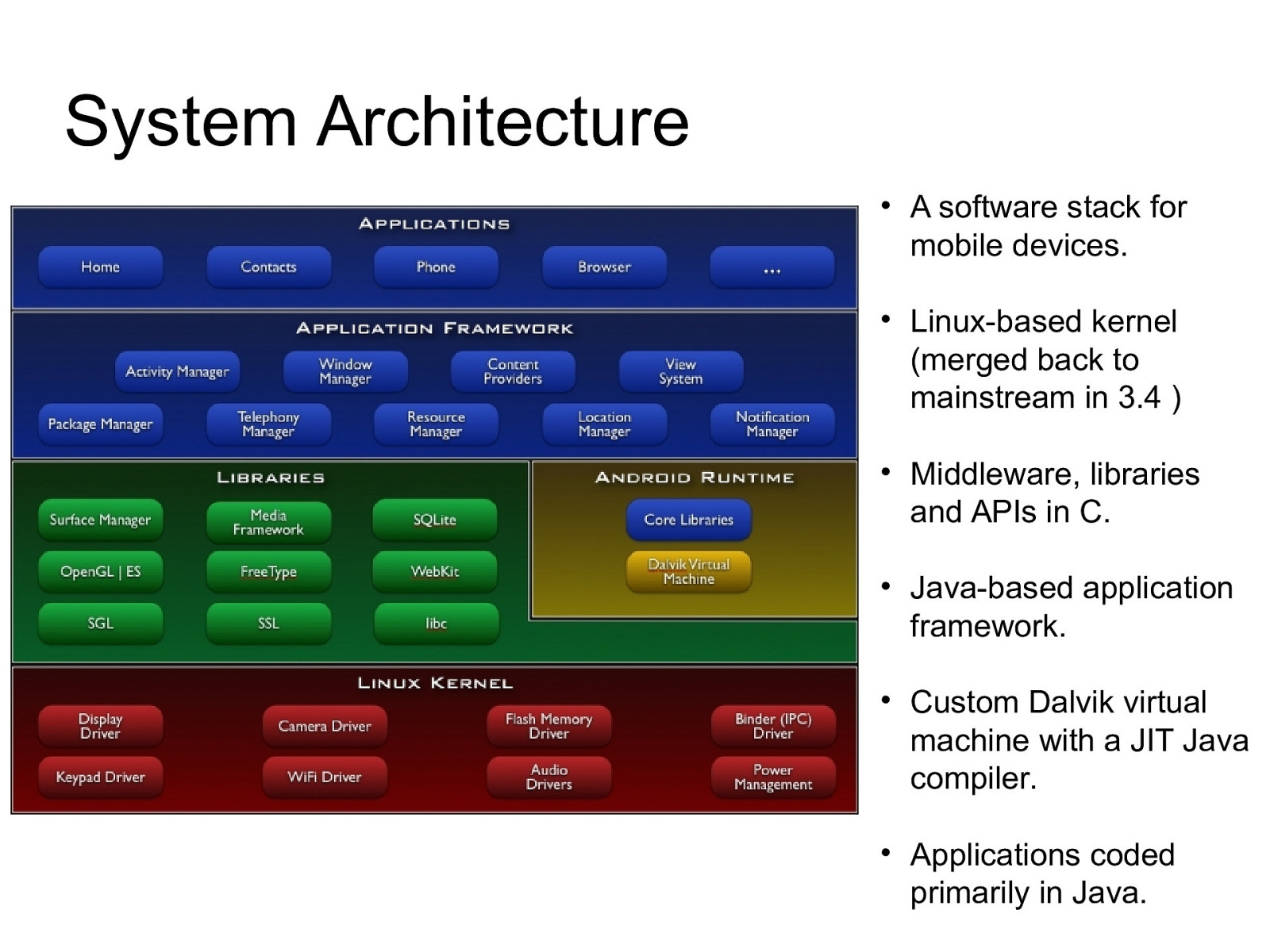
System Architecture • A software stack for mobile devices. • Linux-based kernel (merged back to mainstream in 3.4 ) • Middleware, libraries and APIs in C. • Java-based application framework. • Custom Dalvik virtual machine with a JIT Java compiler. • Applications coded primarily in Java.
Slide 9
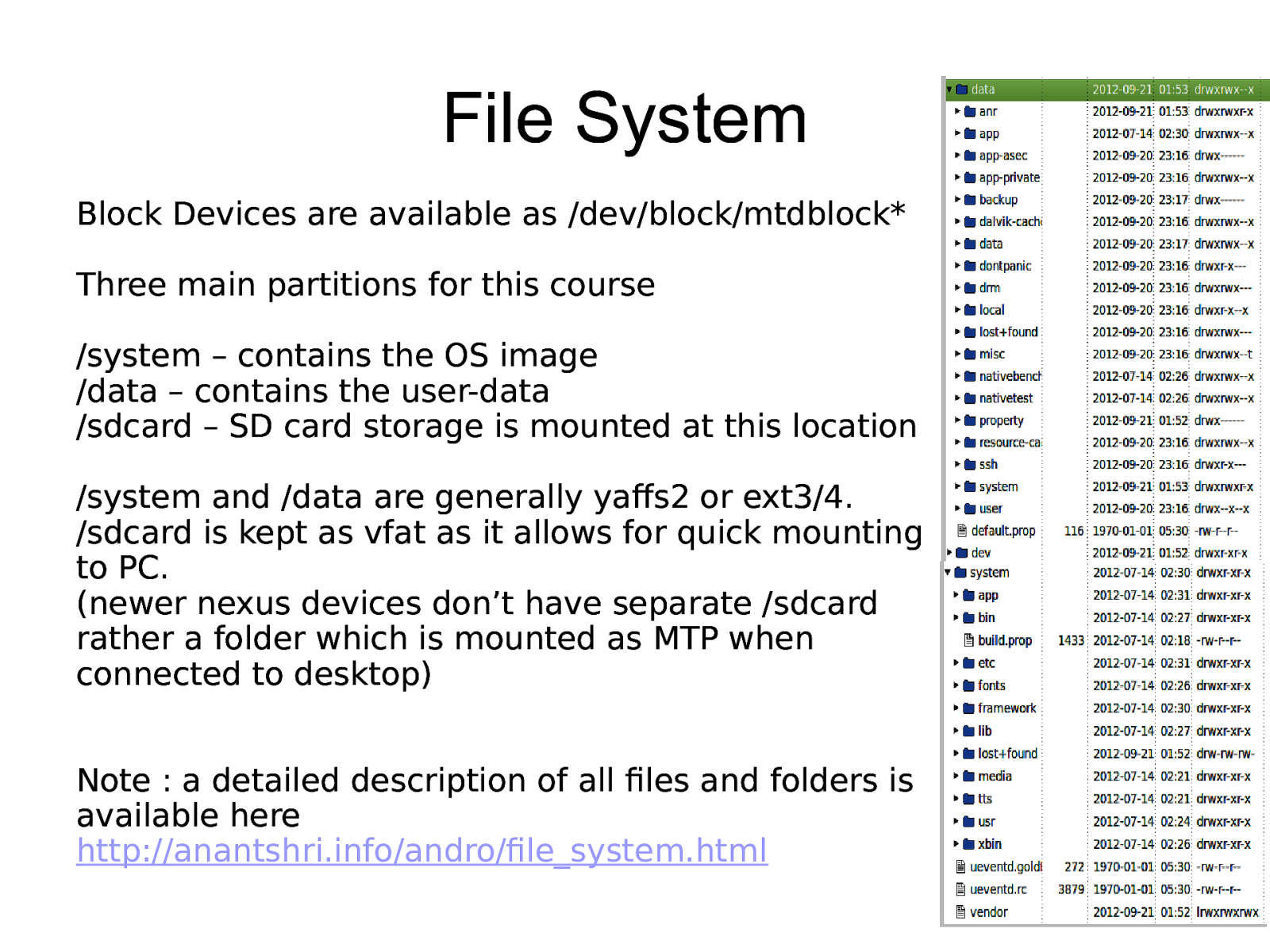
File System Block Devices are available as /dev/block/mtdblock* Three main partitions for this course /system – contains the OS image /data – contains the user-data /sdcard – SD card storage is mounted at this location /system and /data are generally yaffs2 or ext3/4. /sdcard is kept as vfat as it allows for quick mounting to PC. (newer nexus devices don’t have separate /sdcard rather a folder which is mounted as MTP when connected to desktop) Note : a detailed description of all files and folders is available here http://anantshri.info/andro/file_system.html
Slide 10
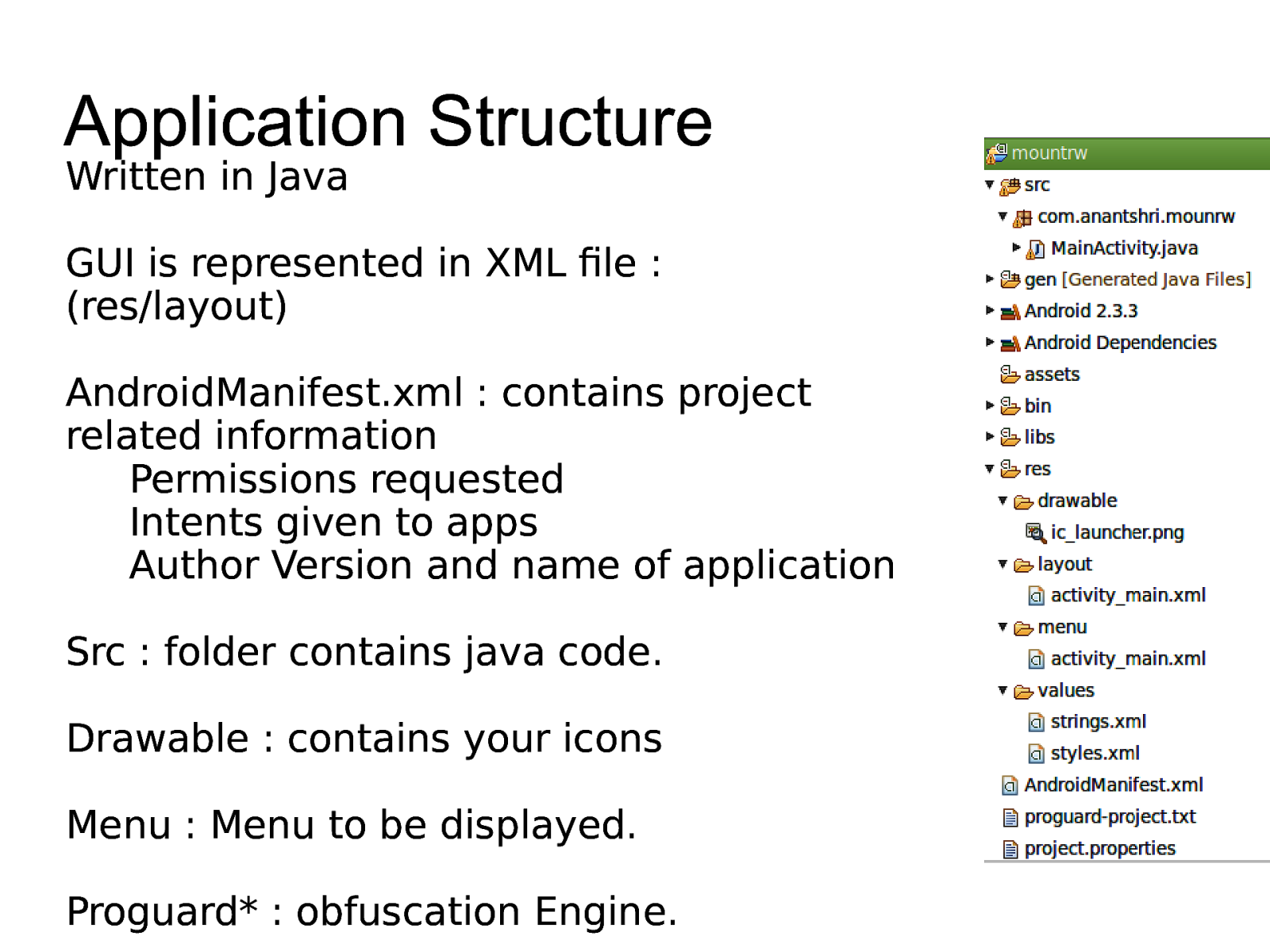
Application Structure Written in Java GUI is represented in XML file : (res/layout) AndroidManifest.xml : contains project related information Permissions requested Intents given to apps Author Version and name of application Src : folder contains java code. Drawable : contains your icons Menu : Menu to be displayed. Proguard* : obfuscation Engine.
Slide 11

Security model System level Unix permission based restriction. SE Linux (4.3 onwards : Permissive mode in 4.3 plans to go enforced in next release) App sandboxing each application a unique id Permission Model Permission need to be taken first time (AppOps introduced as hidden feature in market and can be leveraged to fine tune the permission model) Note : Security model will be covered in details in Module 6
Slide 12

Custom Rom’s Due to Open nature people have started creating there own version of android. AOSP – so far only Google devices + Xperia S Cyanogenod (CM) – enhancement of AOSP KANG – enhancement over CM MIUI – Iphonish look for android (initial fork from CM) And many more xda-developers is one hot spot for all of them
Slide 13

Custom Roms The GOOD Faster Update Cycle The BAD Flashing is a tricky process OTA update without data erase (mostly) First install needs a full format of device Better performance and efficiency Warranty generally is considered void when you use custom rom’s. Latest Version Pre Rooted Features might be missing then the stock ROM
Slide 14

ADB : Android Debug Bridge ADB has ability to perform operations on android device remotely. Adb client -> adb server -> adb daemon (Development machine) -> (device) Some common usage push : Push data inside Device pull : Pull data from Device, file / folder install : Install software in device. (apk) logcat : realtime debug messages With Recent version’s adb connects only to verified devices. (verification taken on first connect)
Slide 15
Android : source Environment setup. Python GNU Make SUN JDK 6 Git 1.7 Download Source (14 GB + counting GIT) Setup repo and download source Build modify where ever you need changes and then compile (depending on processor core will take 1hr to 10hrs)
Slide 16
Android : setup In order to work on android you need following 1) Android SDK 2) Android NDK 3) Eclipse + ADT plugin 4) Arm compiler 5) SUN-JDK OR ANDROIDTAMER alone should be sufficient
Slide 17
Alternate Android VirtualMachines • Geanymotion (recommanded) • Virtualbox x86 version of Android • Jar of Beans (community project) • And many more
Slide 18

Android Tamer
Slide 19

Agenda • • • • • • • • What is Android Tamer Tool List Android Emulator Pentesting Toolset Rooting Kits ROM Modding Reverse Engineering Malware Analysis
Slide 20
What is Android Tamer • VM / Live ISO / Installable environment. • Specific focus on Android Security. • First Launched in Dec 2011 @ Clubhack 2011. • Second Release with large set of enhancement • Provides the most extensive Collection of tools for android security.
Slide 21

More • Based on Ubuntu 12.04 Linux Mint 13 – supported till 2017. • Environment customized to keep all tools in path. • Browser loaded with Pentesting toolkit + Bookmarks • All non essential software’s removed. But could be added once installed on local machine. • Next updates will be through repositories only.
Slide 22

Tools List • ROM Modding • – – – – – – – – Rom kitchen – Flashing utility • Rooting – Zergrush (GB) – adb restore (ICS / JB) – APK based rooting options • • Development – Eclipse + ADT – SDK + NDK – Codesourceory c++ • OWASP ZAP proxy BURP proxy Firefox + pentest plugins W3af Mercury Androguard Dex2Jar JD-GUI APKtool Baksmali / smali Bulb Pentesting Framework Wireless Capture – Wireshark – Tcpdump • Forensics – AF logical OSE – Sleuthkit Pentesting – – – – RE and malware Analysis • Practice Lab – Security Compass Lab – Paladian Lab
Slide 23

Rooting kits • ZergRush – Valid for GingerBread • Superoneclick – Zergrush – psneuter • Gingerbreak • Z4root • superandRoot
Slide 24

ROM Modding • ROM Kitchen – Allows to modify existing ROMs add or remove content or modify settings (ro.secure=?) • Flashing Utilities – Flashtool :SONY Xperia Series – Heimdall : SAMSUNG Galaxy Series – SBP_flash : MOTOROLA phones • Single Click ADB SHELL and LOGCAT access
Slide 25
Reversing toolset • JD-GUI • JED • DEX2JAR • Smali / Baksmali • APKtool
Slide 26

Malware Analysis • DroidBox • Mercury • Androguard
Slide 27

More to come • Android Tamer has its own space now http://androidtamer.com • Keep watching the space for more updates in forms of – Tutorials – How-to’s – New tools.
Slide 28

Android Application Architecture
Slide 29

Agenda ● Dalvik Virtual machine ● App components ● Android SDK, NDK and tools ● Hello World App
Slide 30

Dalvik Virtual Machine ● Designed and written by Dan Bornstein ● Virtual machine for running android apps ● ● ● ● Android apps written in Java, compiled and converted to Dalvik bytecode format (dex – Dalvik Executable) Dalvik bytecode different from Java bytecode Dalvik was created to for computers with memory and performance constraints Dalvik is a registerbased VM as apposed to stack based VM for Java and uses a different instruction set
Slide 31
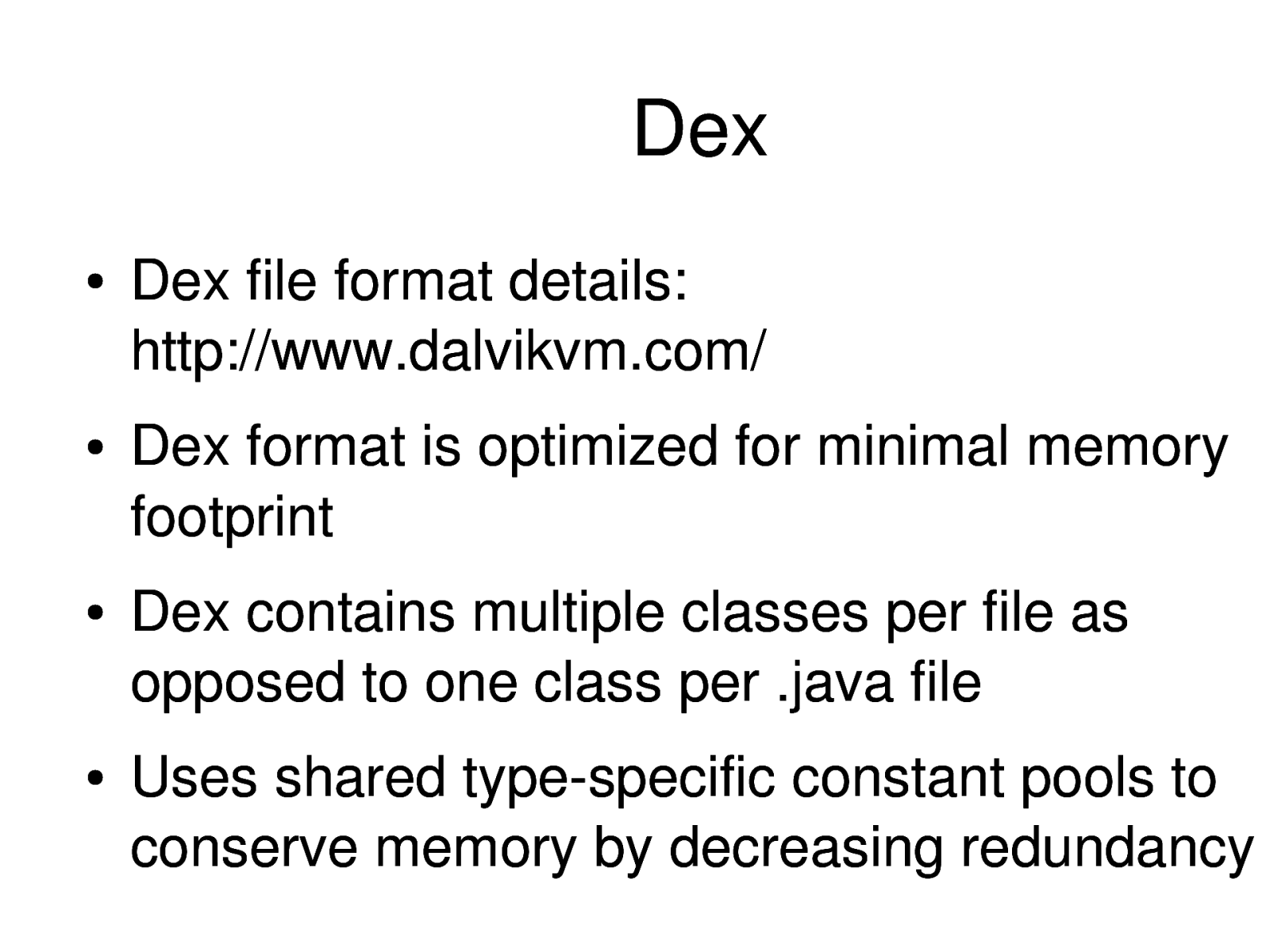
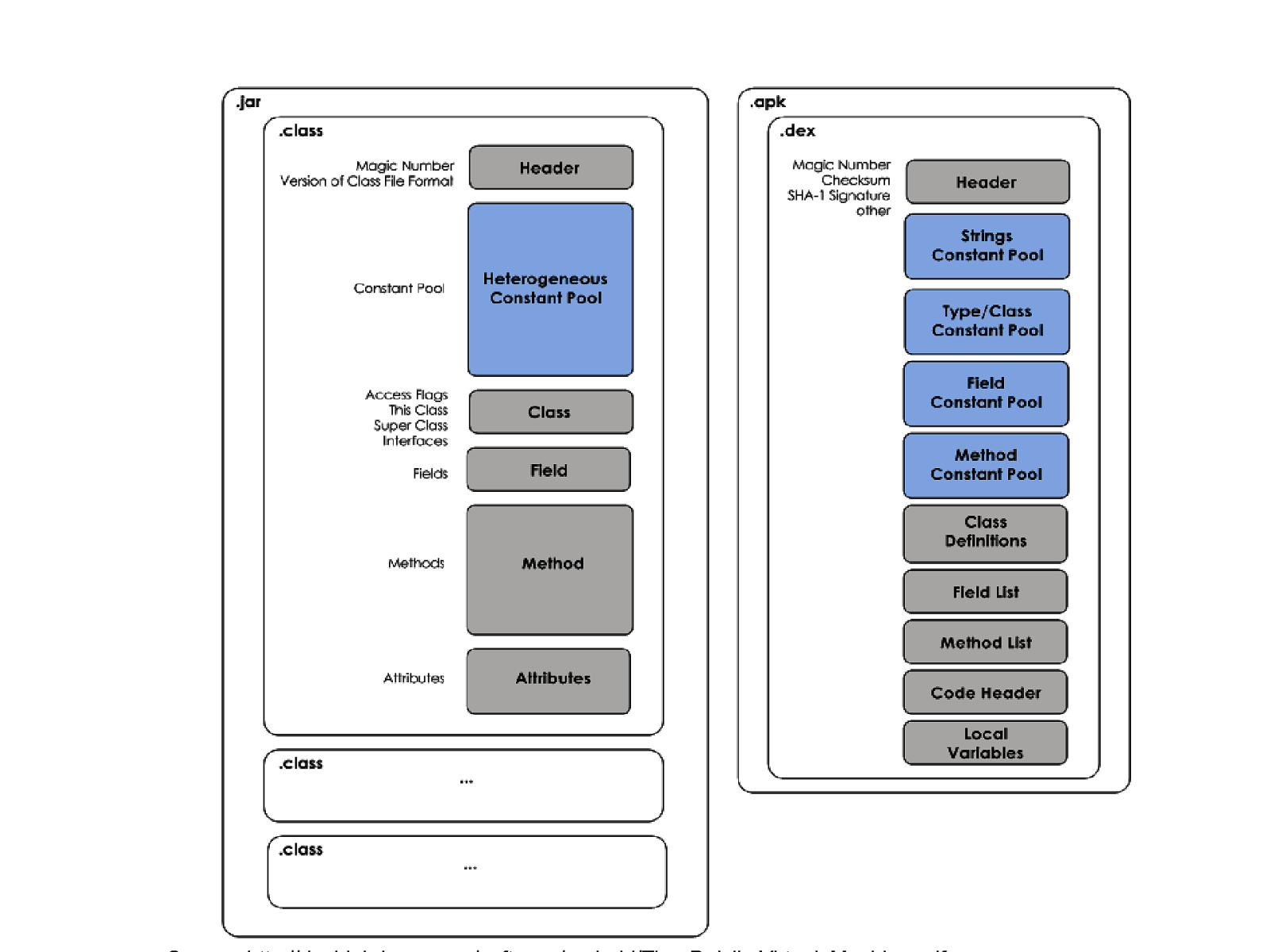
Dex ● ● ● ● Dex file format details: http://www.dalvikvm.com/ Dex format is optimized for minimal memory footprint Dex contains multiple classes per file as opposed to one class per .java file Uses shared typespecific constant pools to conserve memory by decreasing redundancy
Slide 32
Slide 33
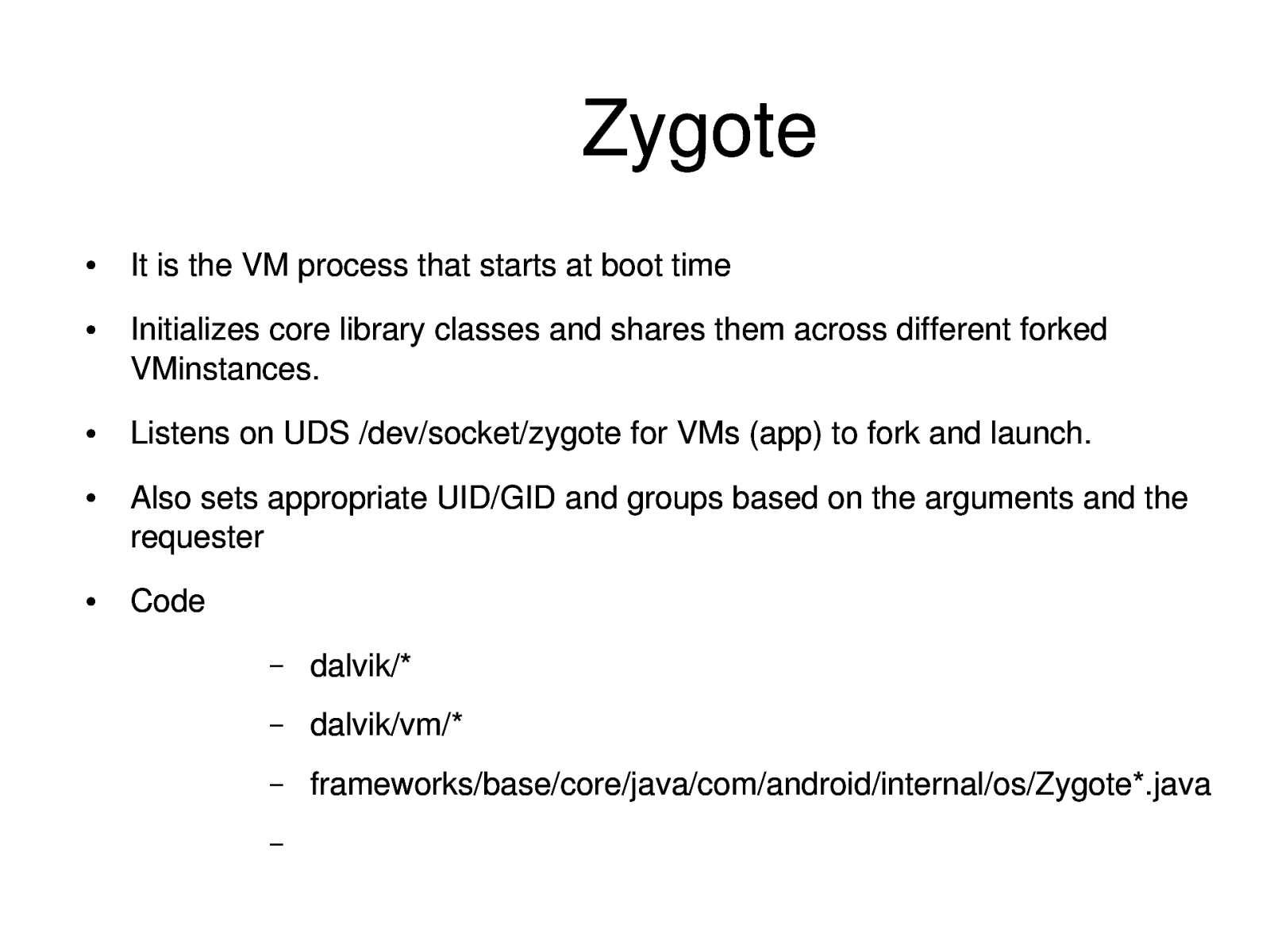
Zygote ● ● ● ● ● It is the VM process that starts at boot time Initializes core library classes and shares them across different forked VMinstances. Listens on UDS /dev/socket/zygote for VMs (app) to fork and launch. Also sets appropriate UID/GID and groups based on the arguments and the requester Code – dalvik/* – dalvik/vm/* – frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote*.java –
Slide 34

Agenda ● Dalvik Virtual machine ● App components ● Android SDK, NDK and tools ● Hello World App
Slide 35

App components ● Activity ● Intent ● Service ● AndroidManifest.xml
Slide 36

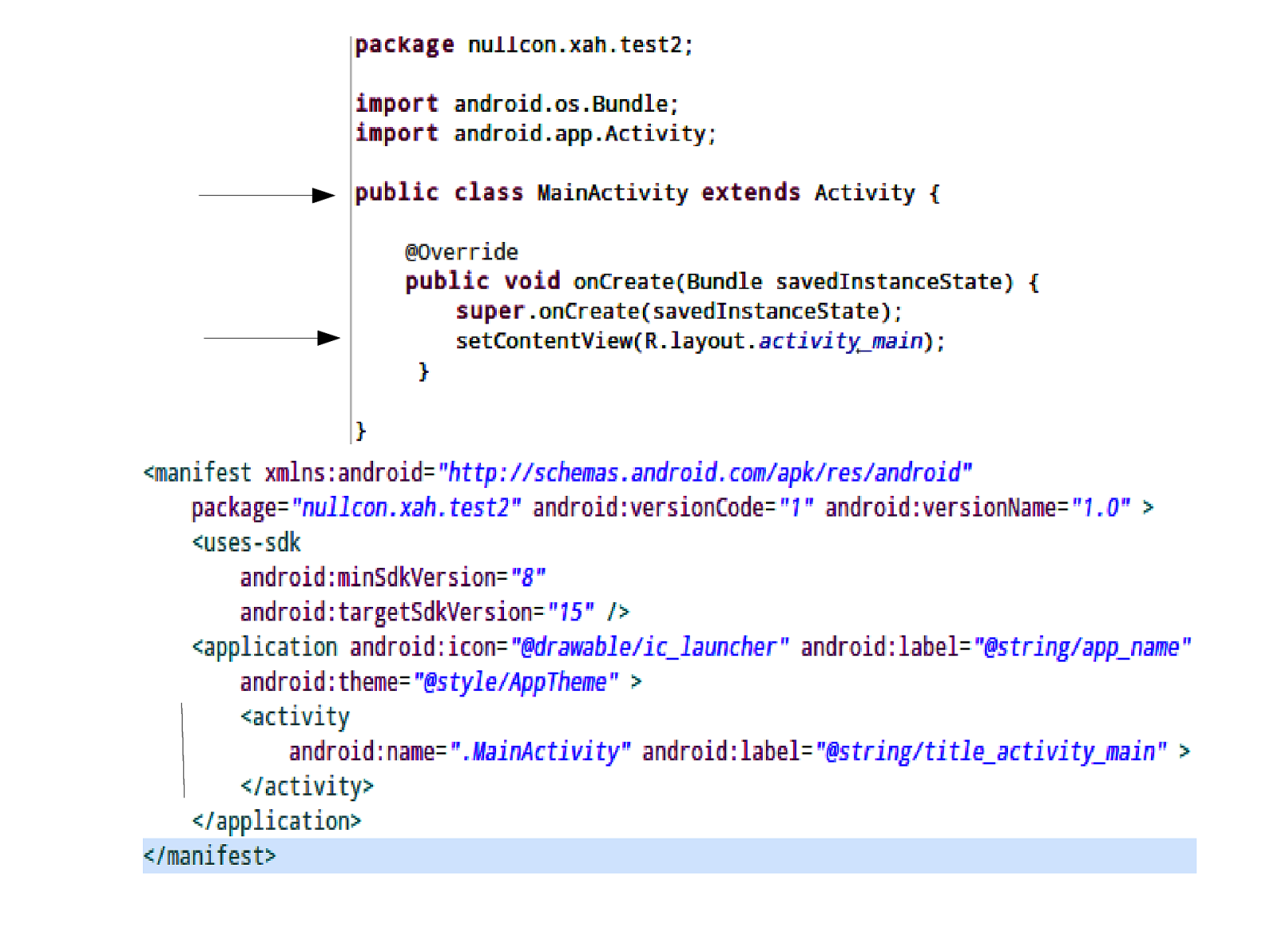
Activities ● UI component for one focused task ● Usually a single screen in your application ● ● Stack based approach where visible activity/screen is topmost activity on stack. Activity association is defined in the AndroidManifest.xml
Slide 37
Slide 38
Intent ● Intents ==Operations / Actions ● Defined in Manifest (AndroidManifest.xml) ● application → activity → intentfilter
Slide 39
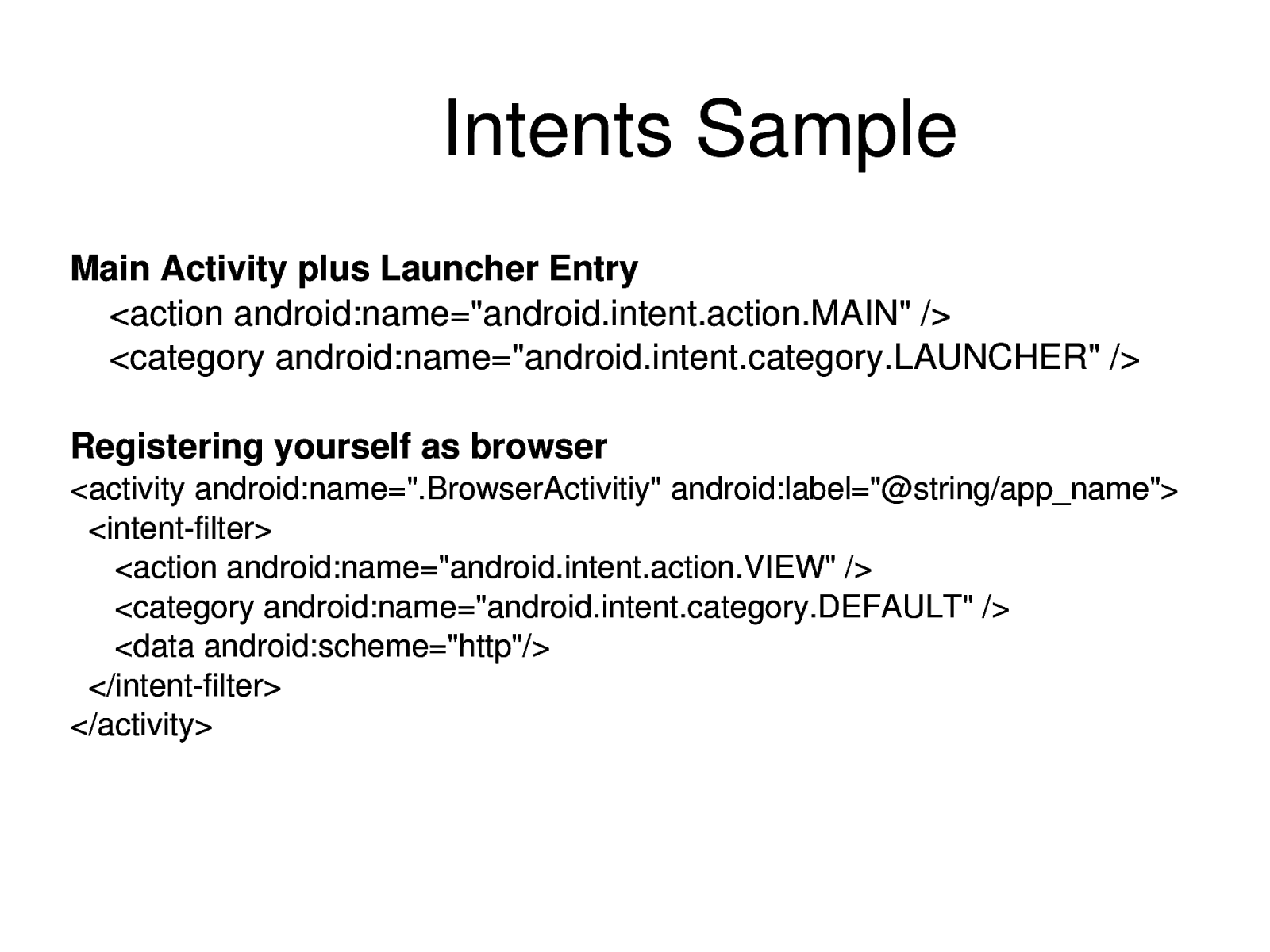
Intents Sample Main Activity plus Launcher Entry <action android:name=”android.intent.action.MAIN” /> <category android:name=”android.intent.category.LAUNCHER” /> Registering yourself as browser <activity android:name=”.BrowserActivitiy” android:label=”@string/app_name”> <intentfilter> <action android:name=”android.intent.action.VIEW” /> <category android:name=”android.intent.category.DEFAULT” /> <data android:scheme=”http”/> </intentfilter> </activity>
Slide 40

Service ● Background Jobs ● No UI ● Long running process. No effect on response. ● Declare Service application → service <service android:name=”.ExampleService” /> ● extends IntentService ● protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent)
Slide 41

Android Manifest.xml ● XML structure defining properties including – Activities – Intents – Userpermissions
Slide 42

Android Manifest.xml <usespermission /> list of required permissions from OS. <permission /> list of permission calling party must have. <usessdk /> min max and target sdk versions. <usesconfiguration /> hard and software configuration <usesfeature /> specific features (filters) <application> <activity> activities provided by the application <intentfilter> various intents raised by application <service> background activity. <receiver> catch holder for system / broadcast intents.
Slide 43

Agenda ● Dalvik Virtual machine ● App components ● Android SDK, NDK and tools ● Hello World App
Slide 44
Android SDK, NDK and tools ● SDK – Software Development Toolkit.
Slide 45
Android SDK, NDK and tools ● ● NDK – native development kit – Allows development of components in C / C++. – allows reuse existing code libraries. – possibly increased performance. Typical usage – selfcontained, – CPUintensive operations, – signal processing, – physics simulation – GAMES
Slide 46
Tools provided by SDK / NDK ● GCC compiler for ARM (usage will be covered in ARM assembly primer) ● Tools → android → sdk/avd manager ● Tools → ddms → debugging tool ● Tools → emulator → emulator executable ● Platformtools → adb → debug bridge ● Platformtools → fastboot → flashing utility
Slide 47

Agenda ● Dalvik Virtual machine ● App components ● Android SDK, NDK and tools ● Hello World App
Slide 48

Hello World App ● ● Exercise A simple application which prints hello world using a label with eclipse
Slide 49

References ● ● Dalvik VM: http://davidehringer.com/software/android/The _Dalvik_Virtual_Machine.pdf https://developer.android.com/guide/
Slide 50

Pen Testing
Slide 51

Agenda • Understanding Mobile Security Issues • Setup Pen testing environment
Slide 52

Mobile Security Issues
Slide 53

Agenda Data / Activity Sniffing Unauthorized access to telephony layer (dialing, sms etc) Unauthorized network access Unsafe Data at transit / rest (XML / SQlite) Hardcoded values Password / key / salt Untrusted inputs / intents Data leakage Side channel Information Disclosure Logic / Time Bomb UI impersonation Rooting Application Security update cycles OS level security updates HTML 5 attacks SQLi Click / Tap jacking Playing with Javascript
Slide 54

Data / Activity Sniffing • Data and activities could be monitored on real time – – – – – – – – – Messaging (SMS and Email) Audio (calls and open microphone recording) Video (still and full-motion) Location Contact list Call history Browsing history Input Data files • Example :Secret SMS Replicator
Slide 55
Access to telephony layer • Malware now a days are targeting SMS / Calls. • Premium SMS / Call -> high charge • USSD based purchases • Location specifics • Example – FakePlayer : Premium SMS sending app
Slide 56

Unsafe data at transit • Data Transmitted using insecure Channels. – HTTP – FTP – Unsigned XML • Protection : Use HTTPS • Ever Heard of sslstrip ?
Slide 57

Hardcoded values • Reverse Engineer the source Code and check for hardcoded values – Db connection strings – Api keys for third party apps.
Slide 58

Side channel leakage • Data leakage occurring through residual data like cache or temp files or keylogers. • Root Cause – Bad coding practice from developer. – Inherent OS specific features. • Identification Techniques – Before launching application take a snapshot of system. Launch application perform all operations and then again take a snapshot. Find the change in system look for residual file and data specially in temporary folders. • Action / Remediation: – Avoid web data caching by setting proper headers.
Slide 59

Information disclosure This risk is based on the fact that many developers hardcode the API or password, also lots of applications are now shifting business logic to client side. • Root Cause – Most of the web applications could be easily reverse engineered. – Hardcoded API Keys, passwords and other sensitive information. – Embedding business logic in client code. • Identification Techniques – Decompile application and check if some hardcoded values are visible and if business logic could be altered. (especially in case of financial applications) • Action / Remediation: – Values should not be hardcoded. – Business logic should be kept separate at server side only.
Slide 60
Logic / Time Bomb • Code to be activated – Specific dates – connecting to a network – Dialing a number – Receiving an sms – You can think of some more …….
Slide 61

UI Impersonation • Application Posing as a known legitimate Apps or websites. • Prevention : Google app store has started rejecting and banning applications performing such tactics. (other app stores ??? And side loading)
Slide 62

Rooting • Devices are by default running in a restricted user environment (refer permissions section) • Root user holds ultimate authority over system. • All released android versions are vulnerable. • Exploits used to gain root access are – OS based (Os level binary flaws) – Devices specific files
Slide 63

Application Updates • Application Updates are send over the air. • If update happening over Wifi sniffing is easy. • Google play store may apply security. But not all stores are having all securities in place. • Play store is only available with Google authorized phone manufacturers
Slide 64

OS level updates • Android updates are largely carrier and manufacturer dependent. • Google updates AOSP others (manufacturers and carriers) download and distribute. • Only independent devices as of now – Google nexus series – Xperia S (experimental)
Slide 65
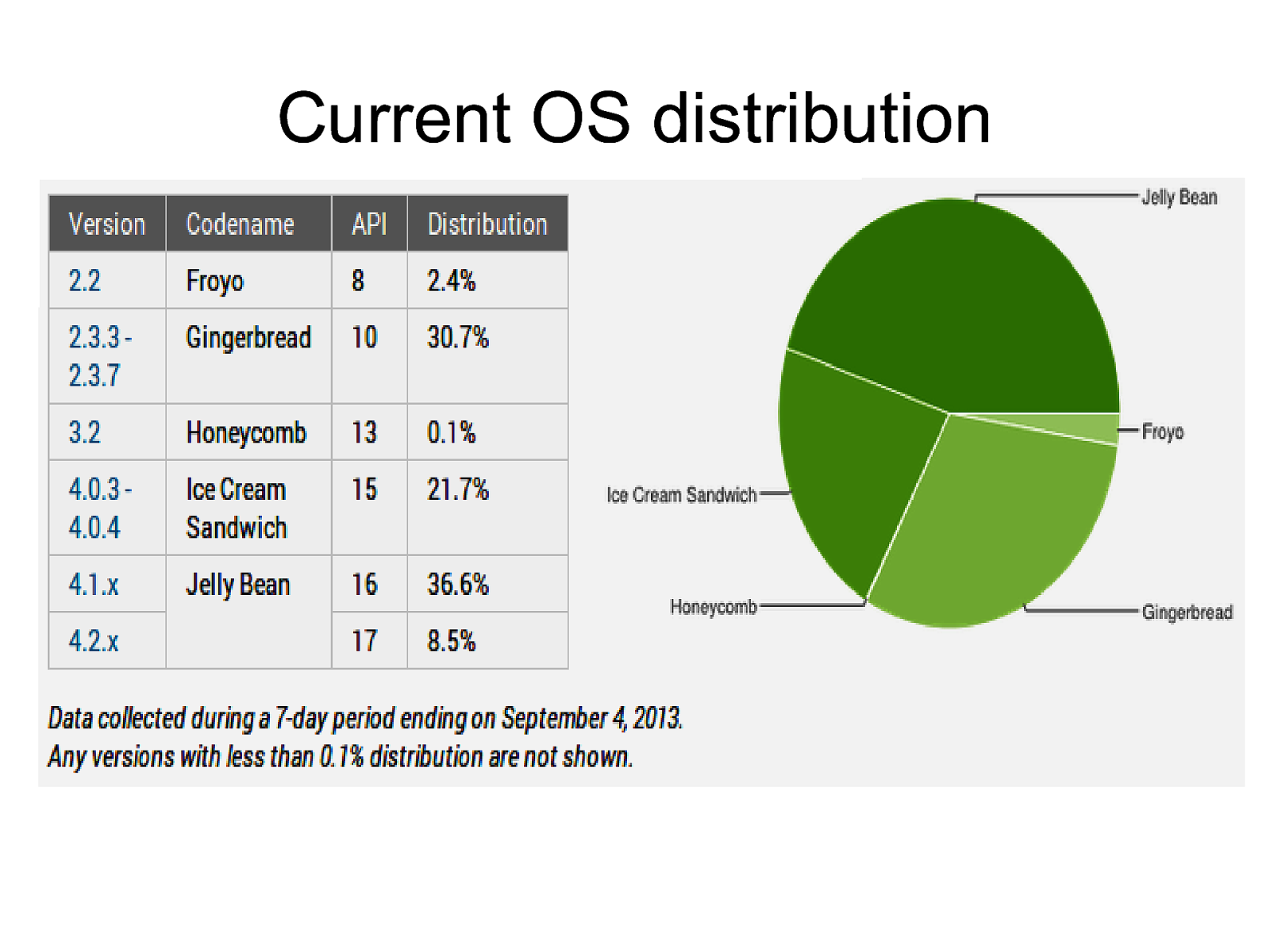
Current OS distribution
Slide 66

SQLi • Large amount of application have backend running on a web server + db server backend. • So tradition SQLi still works the deal is to find the backend.
Slide 67

Click / Tap jacking • Clickjacking for mobile is Tap jacking. • Simmilar techniques like clickjacking. • Transparent frame placed on top of legitimate looking button’s. • Could be used to earn ad revenue on clicks.
Slide 68
Javascript • Javascript is the new playground. • Iframes and various javascript calls are hard to detect on mobile browser. • With HTML5 in picture now the vectors availability has increased multifolds.
Slide 69

Setup Pentesting Environment
Slide 70

Setup • Static Analysis Tools – Reversing the apk • Dex2jar + Jd-gui / jad • Smali • Network traffic interception – OWASP ZAP – Burp suite • Backend and frontend scanning – Emulator as isolated environment. – Server side scanning (nikto, w3af, nmap)
Slide 71

Reversing the APK • APK == JAR == TAR • .dex ~~~ .classes merged • Simplest process – Unzip – Dex2jar convert .dex to jar file – Jd-gui / jad to decompile jar. – Apktools : extract resources and correct binary xml
Slide 72
Network traffic interception • Using emulator or device define proxy. • Emulator –http-proxy http://127.0.0.1:8080 –avd <name> • Settings -> networks -> access point -> proxy host -> port • For emulator localhost / base machine’s ip = 10.0.2.2
Slide 73
Network interception cont… • Issues in listed approach 1) SSL traffic most of the time will not be intercepted and app will crash with connection failure due to invalid certification. 1) Solution is to import the certificate of the proxy server. 2) Export proxy cert from application 3) Adb push .cer /sdcard/ 4) Settings -> security -> install from sdcard 1) Will have to set a pin for device.
Slide 74
Network traffic interception cont.. • Application traffic not proxified For emulator’s this is applicable till 2.3.3 emulator. Tested above settings on 4.0 and 4.1 series and all apps are by default proxified.
Slide 75
Frontend / device scanning • Data by app stored in – /data/data/<app_package_name> • /sdcard content. • Look for xml or db’s for unencrypted data • File system could be scanned for changes before and after install / usage / removal of application
Slide 76
Backend Scanning • During Network interception you can easily identify the backend server ip’s / url’s • nmap,w3af,nikto scan on backend could be made to assess it. • Server side flaws need not be web flaws only, any service running of server could be our potential target.
Slide 77

Summery • APK decompiling – dex2jar jd-gui • | • dynamic analysis exec app in emulator ui / filesystem / | • | network traffic • • • | | backend scanning
Slide 78

Excercise • App Protector. – Protects your phone specific functions from unauthorized access – Or does it. – Refer : /data/data/com.ruimaninfo.approtect/ • Defender – A simple application where you can play and earn powers at offline level and then compete with opponent online.
Slide 79

Pentesting Frameworks ● Mercury / Drozer ● AFE (Android Framework for Exploitation) ● Smartphone Pentest Framework
Slide 80

Pentesting Through Android
Slide 81
Available Toolset ● DroidSheep ● Dsploit ● Interceptor ● Network Discovery ● Shark ● Network Tools ● zAnti
Slide 82
Pentesting through Android ● Setup Environment – SL4A – Py4a – Pl4a – setup standalone shell for them – write basic scripts for python to perform basic operations ● ● ● – username password bruteforce attack task automation using python username enumeration wordpress script creating packages from scripts
Slide 83

Thank You