You secured your code dependencies, is that enough? Anant Shrivastava
Slide 1

Slide 2

Anant Shrivastava ● Chief researcher @ Cyfinoid Research ● 17+ yrs of corporate exposure ● Speaker / Trainer: BlackHat, c0c0n, nullcon, RootConf, RuxCon ● Project Lead: ● ○ Code Vigilant (Code Review Project) ○ Hacking Archives of India, ○ TamerPlatform (Android Security) (@anantshri on social platforms) https://anantshri.info
Slide 3

Question : Have you heard about SOFTWARE SUPPLY CHAIN SECURITY SBOM (SOFTWARE BILL OF MATERIAL) SOURCE COMPOSITION ANALYSIS TOOLS
Slide 4

Why? Incidences • SolarWind • CodeCov • Colonial Pipeline Resultant • EO by US President • NIST SSDF Framework • SLSA by google • 2024 : Cert-in issued guidelines (C) Cyfinoid Research 4
Slide 5
Why now? • Software build automation == quicker release cycle • Automated release cycle == less wait for features • Faster feature release == less inclination to upgrade dependencies • Too much focus on OSS Codebase without helping the maintainers • Impossible segregation of features and bug fixes • Automated notification of vulnerability (hedonic hamster wheel)
Slide 6
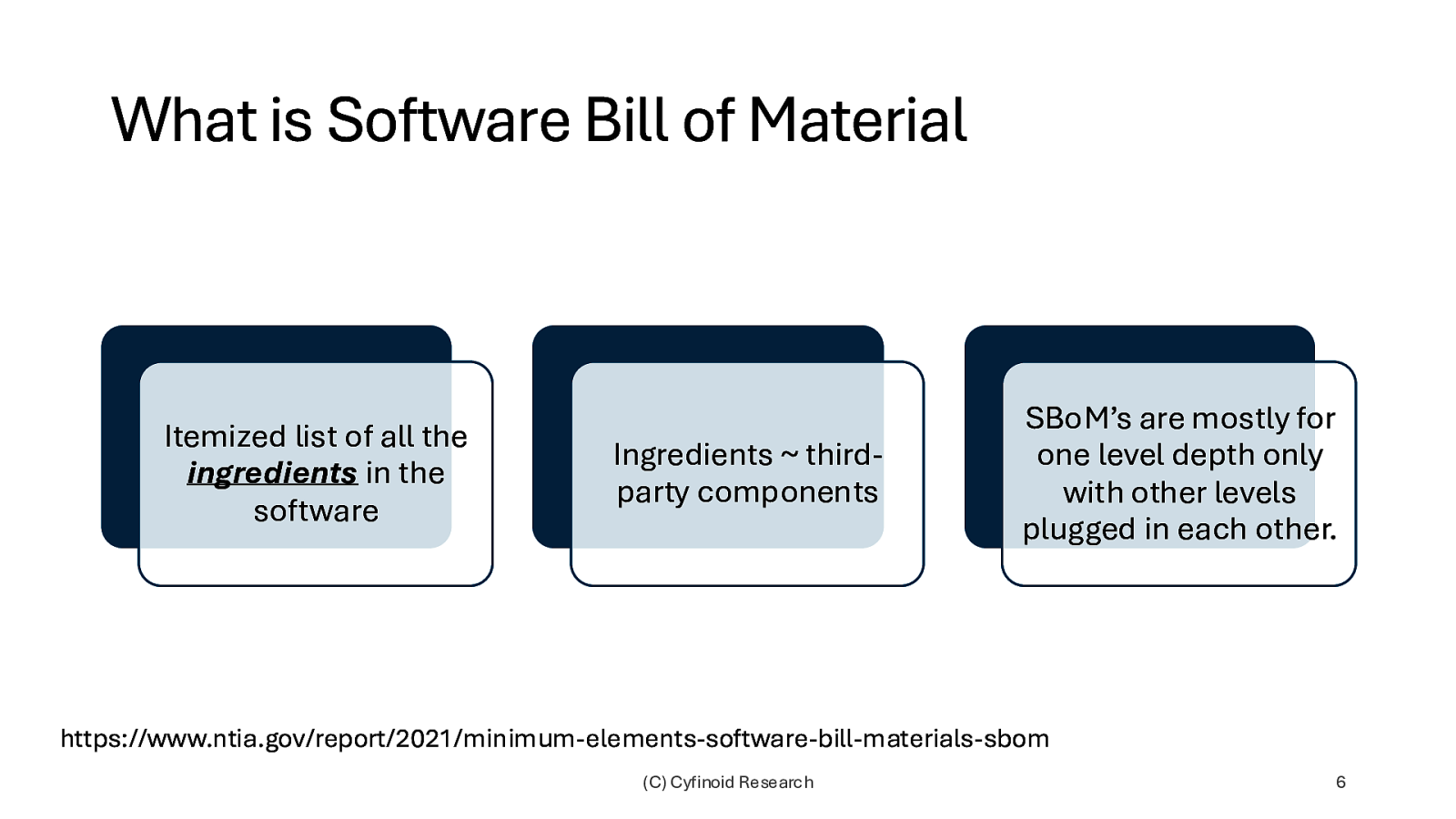
What is Software Bill of Material Itemized list of all the ingredients in the software Ingredients ~ thirdparty components SBoM’s are mostly for one level depth only with other levels plugged in each other. https://www.ntia.gov/report/2021/minimum-elements-software-bill-materials-sbom (C) Cyfinoid Research 6
Slide 7
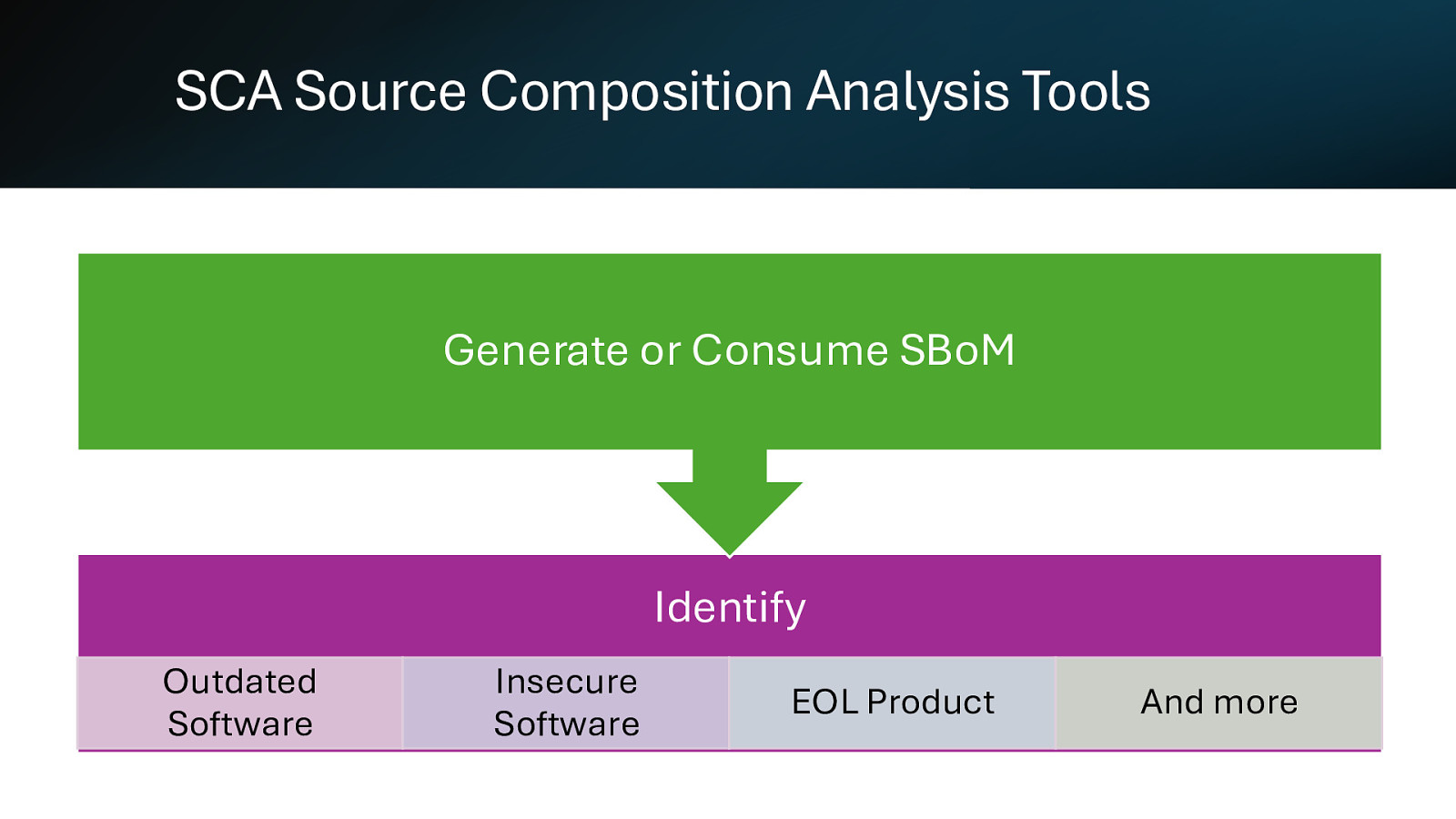
SCA Source Composition Analysis Tools Generate or Consume SBoM Identify Outdated Software Insecure Software EOL Product And more
Slide 8

Question : Raise your hands if You have SCA tooling in your organization? You follow vulnerability management practices for source code components?
Slide 9
Let the fun begin
Slide 10
Software Supply Chains beyond Code chain • We have focused too much on Software code itself • As consumers we are dealing with too many chain not in awareness • As a Company there are dependency chains far beyond code dependencies
Slide 11
What other chains? Any Software or application which allows 3rd party to add or modify functionality pluggable modules / plugins Extensions Theming customizations
Slide 12

Why do they matter PRODUCTION IS HARDENED, DEV NOT SO MUCH EASIER TO COMPROMISE LESS GUARDED PATHS SMALLER ORGS EASIER TO INFILTRATE / OCCUPY / ACQUIRE
Slide 13
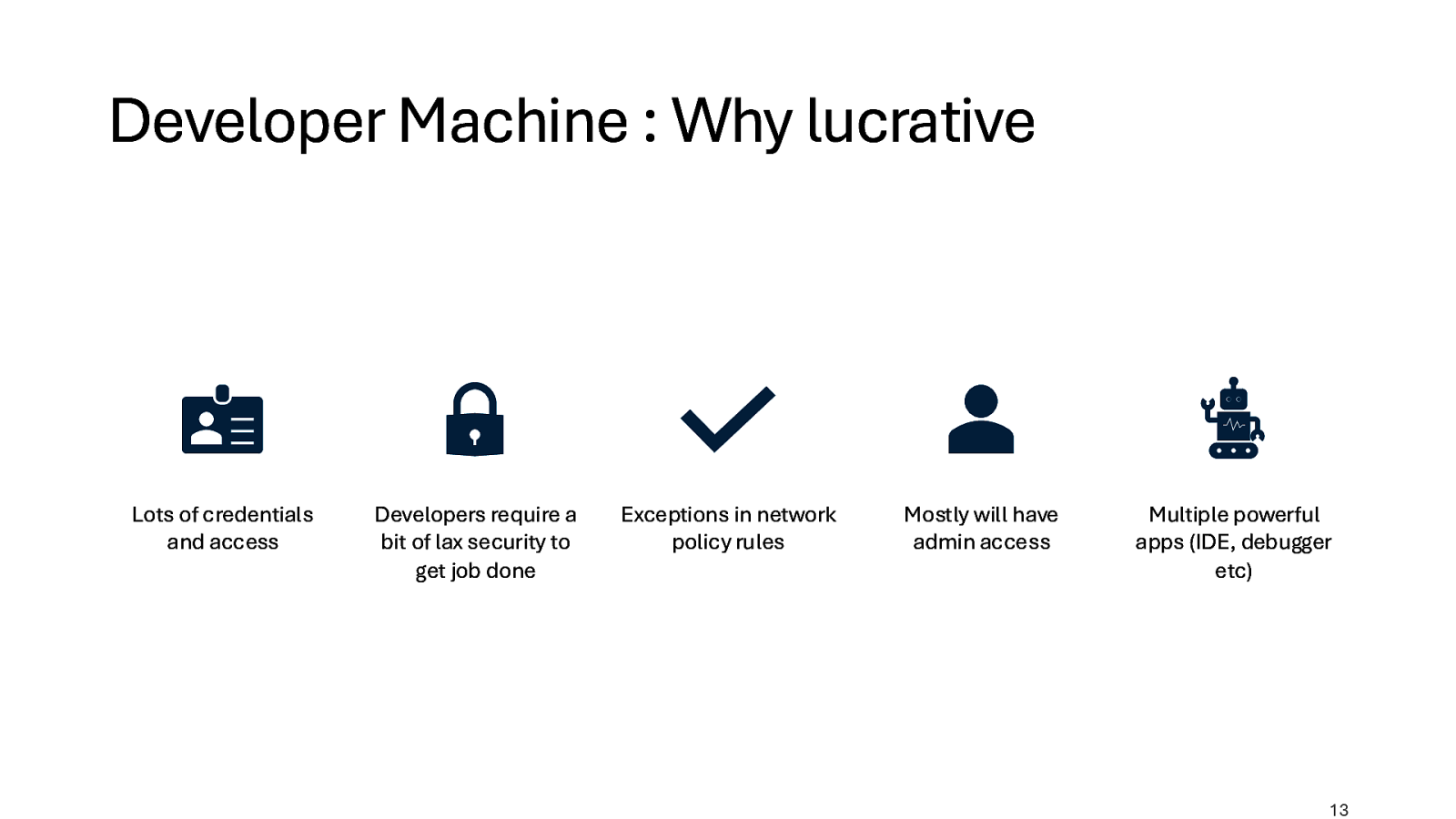
Developer Machine : Why lucrative Lots of credentials and access Developers require a bit of lax security to get job done Exceptions in network policy rules Mostly will have admin access Multiple powerful apps (IDE, debugger etc) 13
Slide 14

Show me data don’t just imagine
Slide 15

Case studies: WYS Is not WYG Content delivered differently to curl and browser : Don’t curl | sh https://jordaneldredge.com/blog/one-way-curl-pipe-shinstall-scripts-can-be-dangerous/ Don’t pipe to shell https://www.seancassidy.me/dont-pipe-to-yourshell.html curl https://anantshri.info/fun/legitimate.sh | bash (C) Cyfinoid Research 15
Slide 16

Chrome Browser • By Google (claimed as fastest) • Installer runs without admin privilege (you can cancel admin prompts) • https://arstechnica.com/security/2025/01/dozens-ofbackdoored-chrome-extensions-discovered-on-2-6-milliondevices/
Slide 17

What can a browser extension do
Slide 18

• https://gbhackers.com/malicious-editthiscookie-extension/
Slide 19
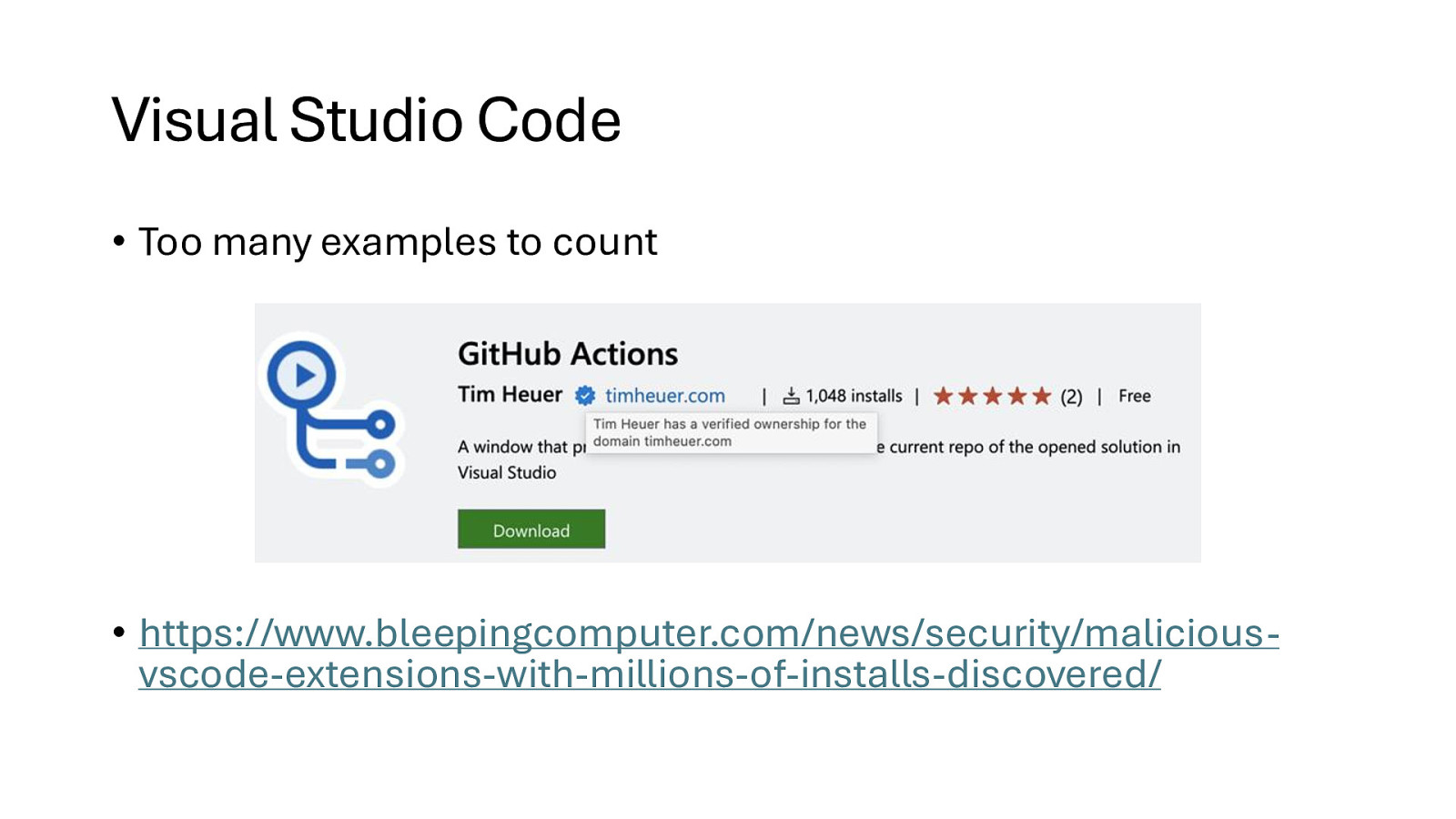
Visual Studio Code • Too many examples to count • https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/maliciousvscode-extensions-with-millions-of-installs-discovered/
Slide 20

Unexpected places for code execution https://manpages.debian.org/bookworm/apt/sources.list.5.en.html https://www.golinuxhub.com/2018/05/how-to-execute-script-at-pre-post-preun-postun-spec-file-rpm/
Slide 21

Unexpected places or code execution
Slide 22
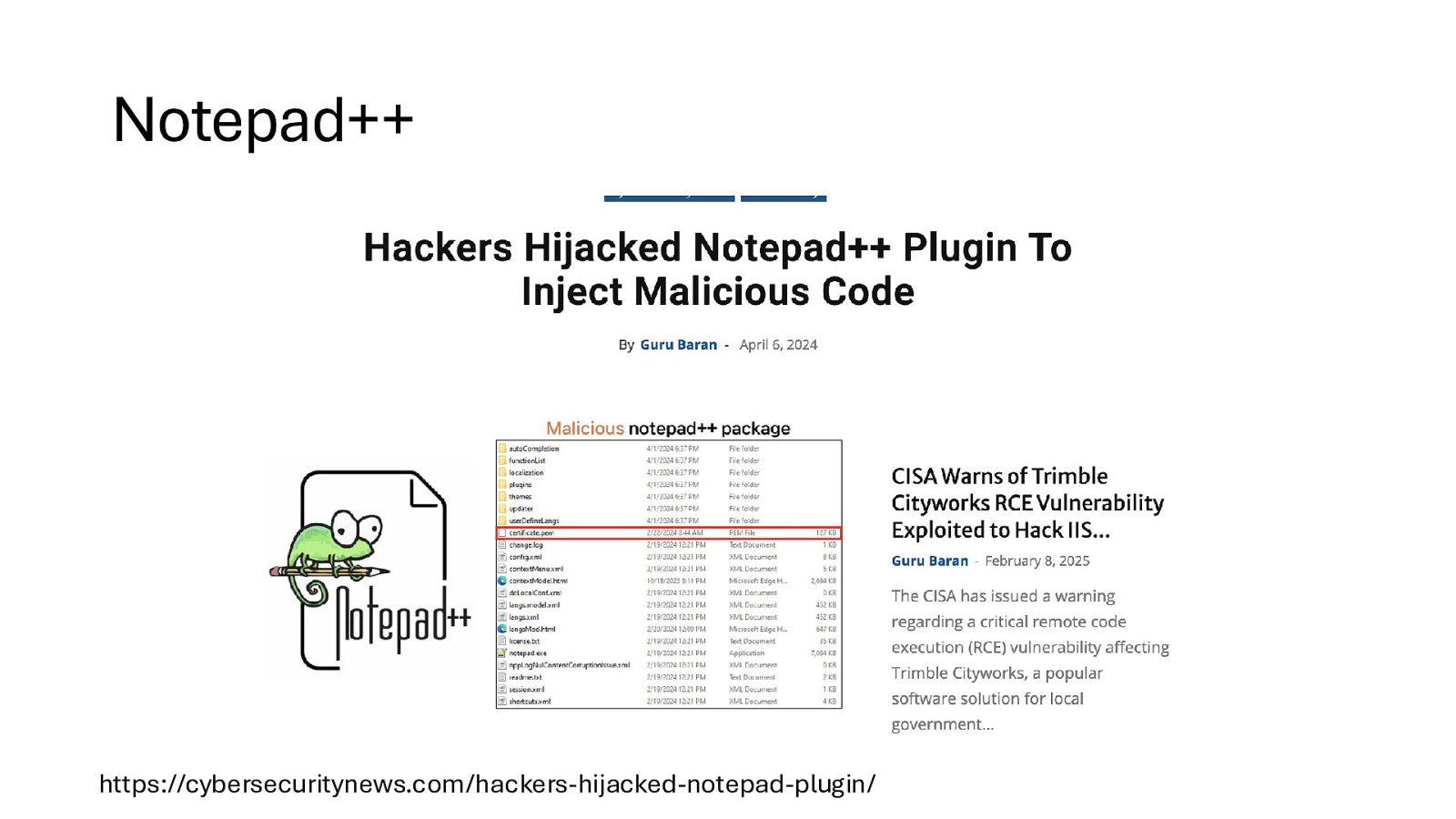
Notepad++ https://cybersecuritynews.com/hackers-hijacked-notepad-plugin/
Slide 23
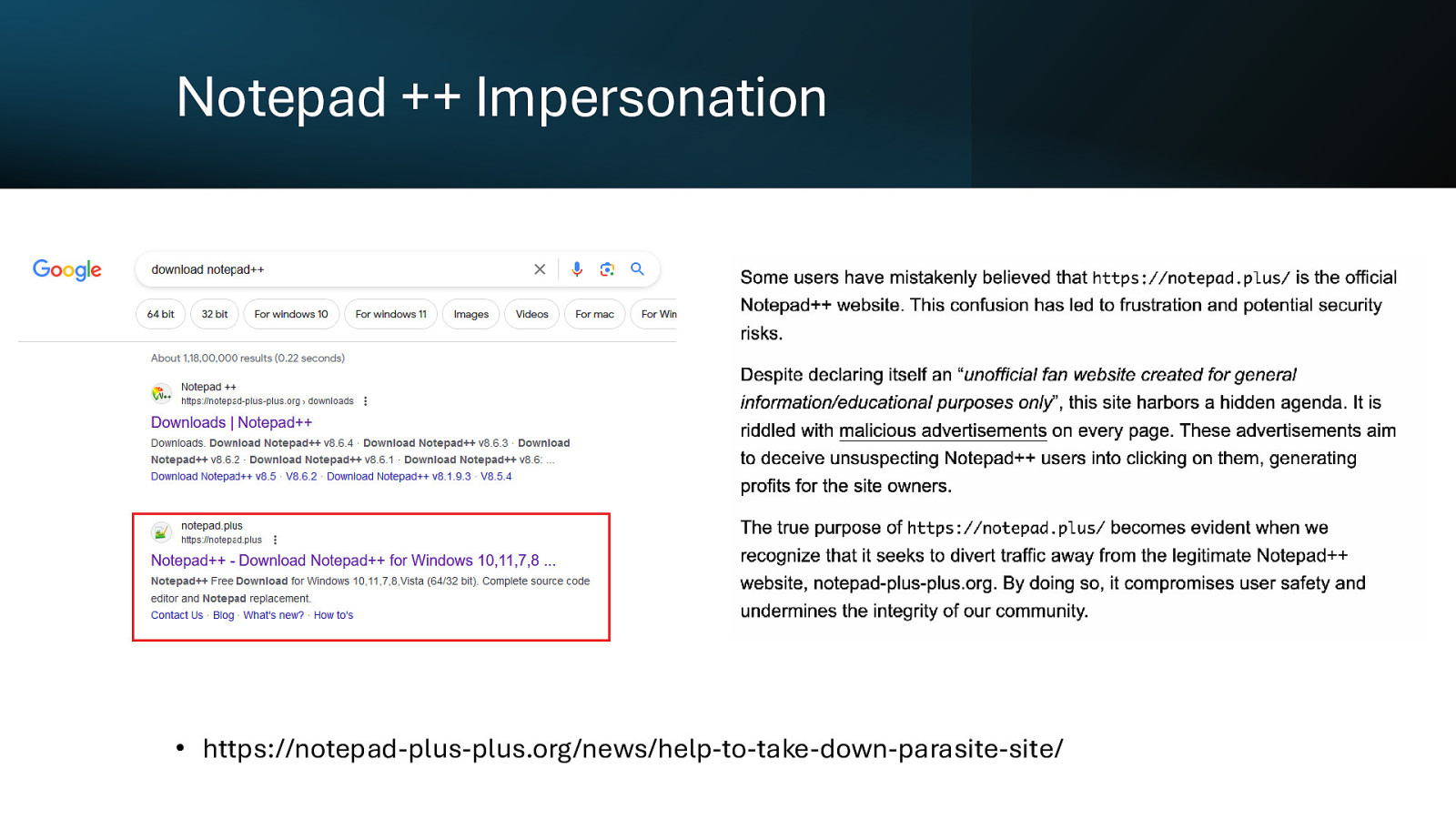
Notepad ++ Impersonation • https://notepad-plus-plus.org/news/help-to-take-down-parasite-site/
Slide 24

C.I. / C.D. Systems • Not just automation • Watch over the entire build or deployment practices • Essential Watchers in the current landscape
Slide 25
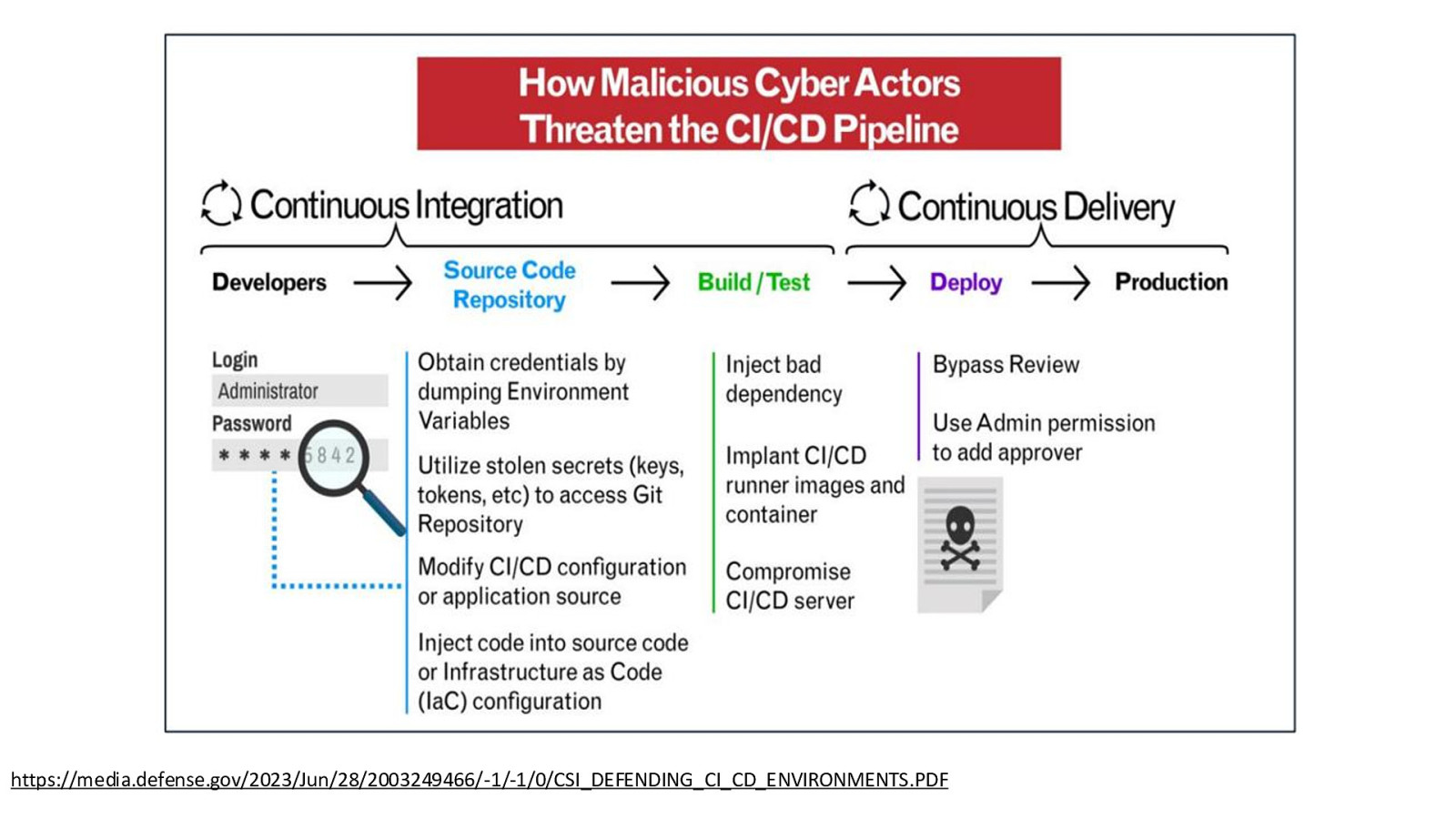
https://media.defense.gov/2023/Jun/28/2003249466/-1/-1/0/CSI_DEFENDING_CI_CD_ENVIRONMENTS.PDF
Slide 26

https://www.darkreading.com/vulnerabilities-threats/global-teamcity-exploitation-opens-door-to-solarwinds-style-nightmare
Slide 27
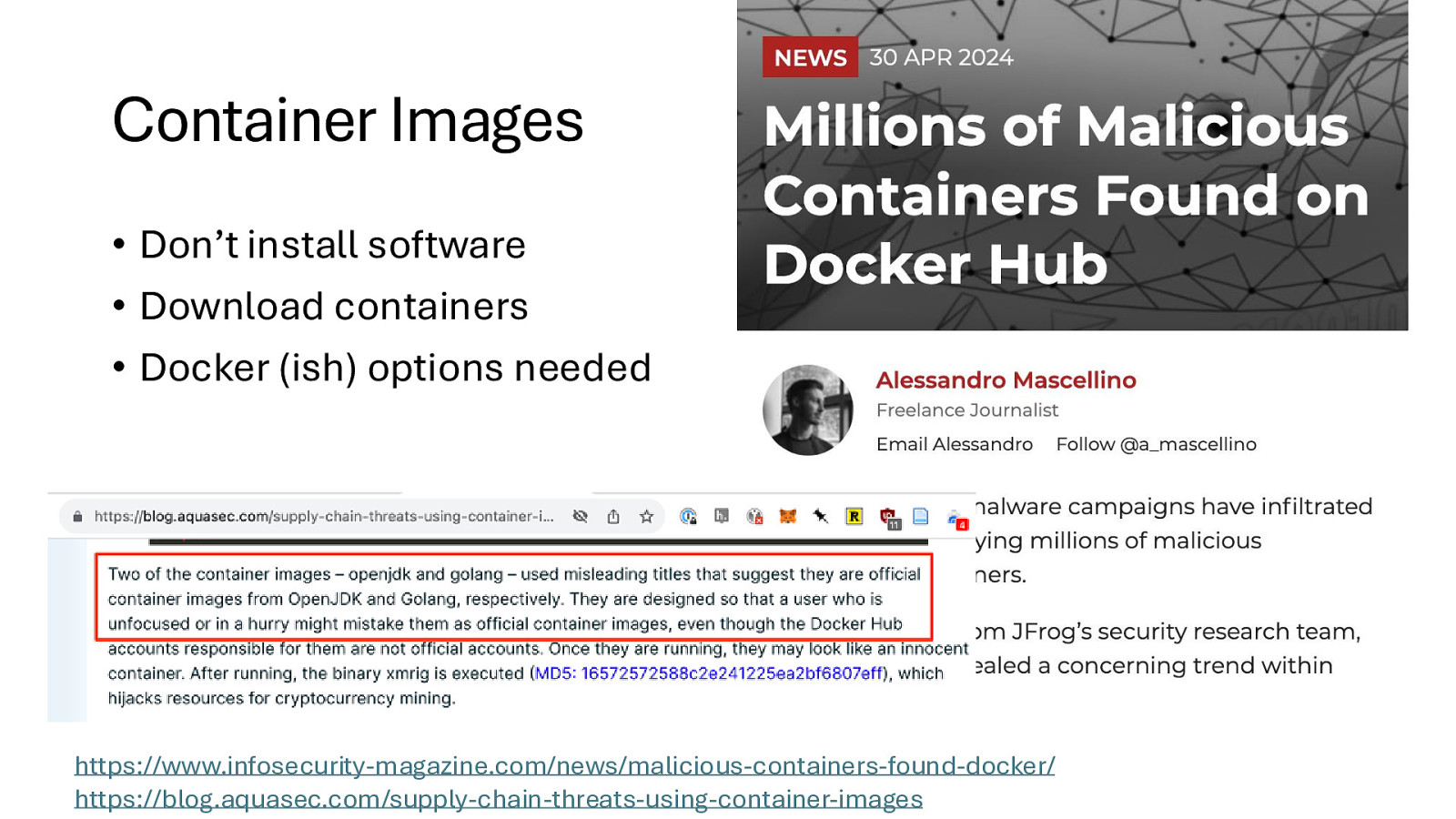
Container Images • Don’t install software • Download containers • Docker (ish) options needed https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/malicious-containers-found-docker/ https://blog.aquasec.com/supply-chain-threats-using-container-images
Slide 28

Dependency Caching Servers https://socket.dev/blog/malicious-package-exploits-go-module-proxy-caching-for-persistence
Slide 29

Bait and Switch Package created with a good intent but later abused Wordpress free plugin purchased and backdoored • https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/backdoorfound-in-wordpress-plugin-with-more-than-300-000installations/ 29
Slide 30

Rogue Maintainers peacenotwar module sabotages npm developers in the node-ipc package to protest the invasion of Ukraine Overwrite all files with if origin is Russia or Belarus. Malware Civil War - 25 malicious packages in npm, with some posing as “colors.js,” and even an instance of malware authors targeting each other through a package called “lemaaa” designed to manipulate Discord accounts. Open source developer corrupts widely-used libraries, affecting tons of projects - For packages color.js and faker.js, the maintainer pushed a corrupt update that triggers an infinite loop of weird characters. 30
Slide 31
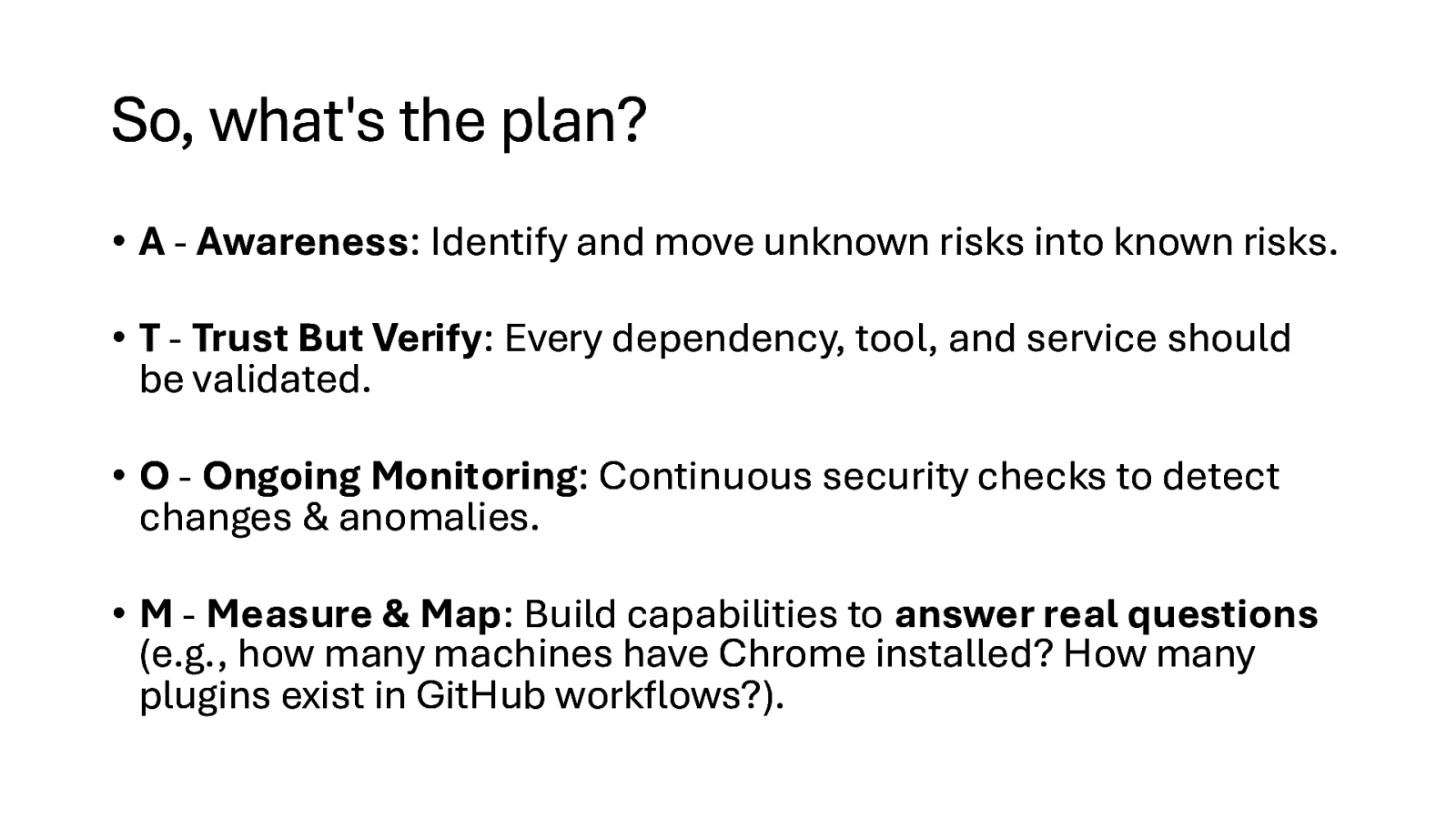
So, what’s the plan? • A - Awareness: Identify and move unknown risks into known risks. • T - Trust But Verify: Every dependency, tool, and service should be validated. • O - Ongoing Monitoring: Continuous security checks to detect changes & anomalies. • M - Measure & Map: Build capabilities to answer real questions (e.g., how many machines have Chrome installed? How many plugins exist in GitHub workflows?).
Slide 32
Can of worms that I have not touched
Slide 33

Thanks for listening & open to Questions? (C) Cyfinoid Research 33